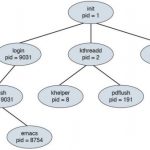
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: Linux- and Mac OS X–Based Analysis Q1. Which process type occurs when a parent process is terminated and the remaining child process is permitted to continue on its own? A. Zombie process B. Orphan process C. Rogue process D. Parent process Answer: B. An orphan process results when a parent process is terminated and the remaining child process is … [Read more...]
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: Introduction to Security Operations Management
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: Introduction to Security Operations Management Q1. In which phase of the identity and account life cycle are the access rights assigned? A. Registration B. Access review C. Privileges provisioning D. Identity validation Answer: C. Access rights are provided during the privileges provisioning phase. Q2. What is an advantage of a system-generated … [Read more...]
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: Fundamentals of Networking Protocols and Networking Devices
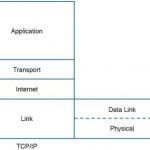
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: Fundamentals of Networking Protocols and Networking Devices Q1. Which layer of the TCP/IP model is concerned with end-to-end communication and offers multiplexing service? A. Transport B. Internet C. Link layer D. Application Answer: A. The transport layer is concerned with end-to-end communication and provides multiplexing through the use of … [Read more...]
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: Introduction to Access Controls
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: Introduction to Access Controls Q1. What entity requests access to a resource? A. Object B. Subject C. File D. Database Answer: B. A subject is the active entity that requests access to a resource. Q2. In which phase of the access control does a user need to prove his or her identity? A. Identification B. Authentication C. Authorization D. … [Read more...]
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: Windows-Based Analysis
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: Windows-Based Analysis Q1. Which of the follow best describes Windows process permissions? A. User authentication data is stored in a token that is used to describe the security context of all processes associated with the user. B. Windows generates processes based on super user–level security permissions and limits processes based on predefined user … [Read more...]
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: Intrusion Event Categories
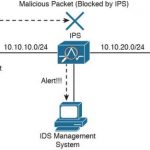
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: Intrusion Event Categories Q1. Which of the following is not true about the Diamond Model of Intrusion? A. Adversaries use an infrastructure or capability to access a victim. B. Meta-features are not a required component of the Diamond Model. C. Technology and social metadata features establish connections between relations. D. A diamond … [Read more...]
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: The Art of Data and Event Analysis
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: The Art of Data and Event Analysis Q1. Which of the following is the process of capturing, storing, and analyzing data so that it exists in only one form? A. Data normalization B. Data correlation C. Big data analytics D. Retrospective analysis Answer: A. Data normalization is the process of capturing, storing, and analyzing data (security-related … [Read more...]
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: Network and Host Profiling
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: Network and Host Profiling Q1. Which of the following is true about NetFlow? A. NetFlow typically provides more details than sFlow. B. NetFlow typically contains more details than packet capturing. C. NetFlow is not available in virtual networking environments. D. NetFlow is only used as a network performance measurement. Answer: A. sFlow (also called … [Read more...]
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: Security Evasion Techniques
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: Security Evasion Techniques Q1. Which of the following is when the attacker sends traffic slower than normal, not exceeding thresholds inside the time windows the signatures use to correlate different packets together? A. Traffic insertion B. Protocol manipulation C. Traffic fragmentation D. Timing attack Answer: D. This example represents adjusting … [Read more...]
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: Types of Attacks and Vulnerabilities
CCNA Cyber Ops FAQ: Types of Attacks and Vulnerabilities Q1. Which of the following are examples of vulnerability and port scanners? (Select all that apply.) A. SuperScan B. nmap C. Nexpose D. Nessus Answer: B, C, D. Nexpose, Nessus, and nmap are all vulnerability and port scanners. Q2. How do UDP scans work? A. By establishing a three-way handshake. B. By sending … [Read more...]