CCNP Switch Lab 4-2 Inter-VLAN Routing with an Internal Route Processor and Monitoring CEF Functions
Objective
- Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF).
Background
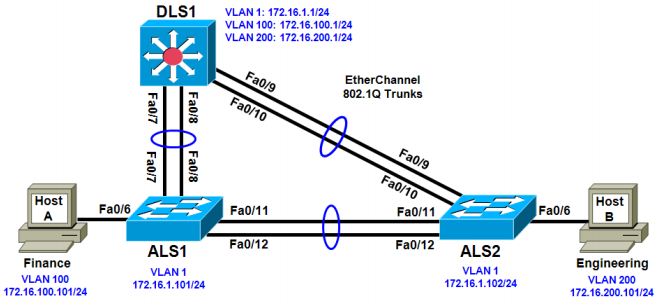
The current network equipment includes a 3560 distribution layer switch and two 2960 access layer switches. The network is segmented into three functional subnets using VLANs for better network management. The VLANs include Finance, Engineering, and a subnet for equipment management, which is the default management VLAN, VLAN 1. After VTP and trunking have been configured for the switches, switched virtual interfaces (SVI) are configured on the distribution layer switch to route between these VLANs, providing full connectivity to the internal network.
Note: This lab uses Cisco WS-C2960-24TT-L switches with the Cisco IOS image c2960-lanbasek9-mz.122- 46.SE.bin and Catalyst 3560-24PS with the Cisco IOS image c3560-advipservicesk9-mz.122-46.SE.bin. You can use other switches (such as 2950 or 3550) and Cisco IOS Software versions if they have comparable capabilities and features. Depending on the switch model and Cisco IOS Software version, the commands available and output produced might vary from what is shown in this lab.
Required Resources
- 2 switches (Cisco 2960 with the Cisco IOS Release 12.2(46)SE C2960-LANBASEK9-M image or comparable)
- 1 switch (Cisco 3560 with the Cisco IOS Release 12.2(46)SE C3560-ADVIPSERVICESK9-mz image or comparable)
- Ethernet and console cables
Step 1: Prepare the switches for the lab.
Erase the startup configuration, delete the vlan.dat file, and reload the switches. Refer to Lab 1 -1, “Clearing a Switch” and Lab 1 -2, “Clearing a Switch Connected to a Larger Network” to prepare the switches for this lab. Cable the equipment as shown.
Step 2: Configure basic switch parameters.
a. Configure the hostname, password, and optionally, Telnet access on each switch.
Switch(config)# hostname ALS1 ALS1(config)# enable secret cisco ALS1(config)# line vty 0 15 ALS1(config-line)# password cisco ALS1(config-line)# login Switch(config)# hostname ALS2 ALS2(config)# enable secret cisco ALS2(config)# line vty 0 15 ALS2(config-line)# password cisco ALS2(config-line)# login Switch(config) # hostname DLS1 DLS1(config)# enable secret cisco DLS1(config)# line vty 0 15 DLS1(config-line)#password cisco DLS1(config-line)# login
b. Configure management IP addresses on VLAN 1 for all three switches according to the diagram.
ALS1(config)# interface vlan 1 ALS1(config-if)# ip address 172.16.1.101 255.255.255.0 ALS1(config-if)# no shutdown ALS2(config)# interface vlan 1 ALS2(config-if)# ip address 172.16.1.102 255.255.255.0 ALS2(config-if)# no shutdown DLS1(config)# interface vlan 1 DLS1(config-if)# ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 DLS1(config-if)# no shutdown
c. Configure default gateways on the access layer switches. The distribution layer switch will not use a default gateway, because it acts as a Layer 3 device. The access layer switches act as Layer 2 devices and need a default gateway to send management VLAN traffic off of the local subnet.
ALS1(config)# ip default-gateway 172.16.1.1 ALS2(config)# ip default-gateway 172.16.1.1
Step 3: Configure trunks and EtherChannels between switches.
To distribute VLAN and VTP information between the switches, trunks are needed between the three switches. Configure these trunks according to the diagram. EtherChannel is used for these trunks.
EtherChannel allows you to utilize both Fast Ethernet interfaces that are available between each device,
thereby doubling the bandwidth.
a. Configure the trunks and EtherChannel from DLS1 to ALS1. The switchport trunk encapsulation [isl | dot1q] command is used because this switch also supports ISL encapsulation.
DLS1(config)# interface range fastEthernet 0/7 - 8 DLS1(config-if-range)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q DLS1(config-if-range)# switchport mode trunk DLS1(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode desirable
Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 1
b. Configure the trunks and EtherChannel from DLS1 to ALS2.
DLS1(config)# interface range fastEthernet 0/9 - 10 DLS1(config-if-range)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q DLS1(config-if-range)# switchport mode trunk DLS1(config-if-range)# channel-group 2 mode desirable
Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 2
c. Configure the trunks and EtherChannel between ALS1 and DLS1, and for the trunks and EtherChannel between ALS1 and ALS2.
ALS1(config)# interface range fastEthernet 0/11 - 12 ALS1(config-if-range)# switchport mode trunk ALS1(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode desirable
Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 1
ALS1(config-if-range)# exit ALS1(config)# interface range fastEthernet 0/7 - 8 ALS1(config-if-range)# switchport mode trunk ALS1(config-if-range)# channel-group 2 mode desirable
Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 2
d. Configure the trunks and EtherChannel between ALS2 and DLS1, and for the trunks and EtherChannel between ALS2 and ALS1.
ALS2(config)# interface range fastEthernet 0/11 - 12 ALS2(config-if-range)# switchport mode trunk ALS2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode desirable
Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 1
ALS2(config-if-range)# exit ALS2(config)# interface range fastEthernet 0/9 - 10 ALS2(config-if-range)# switchport mode trunk ALS2(config-if-range)# channel-group 2 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 2
e. Verify trunking between DLS1, ALS1, and ALS2 using the show interface trunk command on all switches.



f. Use the show etherchannel summary command on each switch to verify the EtherChannels.
The following is sample output from ALS1. Notice the two EtherChannels on the access layer switches.

On ALS1, which ports are used for channel group 2?
_______________________________________________________________________________
The ports used for channel group 2 are Fa0/7 and Fa0/8.
Step 4: Configure VTP on ALS1 and ALS2.
a. Change the VTP mode of ALS1 and ALS2 to client.
ALS1(config)# vtp mode client Setting device to VTP CLIENT mode.
ALS2(config)# vtp mode client Setting device to VTP CLIENT mode.
b. Verify the VTP changes with the show vtp status command.
The output on ALS2 is similar to that of ALS1.


How many VLANs can be supported locally on the 2960 switch?
_______________________________________________________________________________
In the show vtp status command output, it says 255 VLANs can be supported locally.
Step 5: Configure VTP on DLS1.
a. Create the VTP domain on DLS1 and create VLANs 100 and 200 for the domain.
DLS1(config)# vtp domain SWPOD DLS1(config)# vtp version 2 DLS1(config)# vlan 100 DLS1(config-vlan)# name Finance DLS1(config-vlan)# vlan 200 DLS1(config-vlan)# name Engineering
b. Verify VTP information throughout the domain using the show vlan and show vtp status commands. How many existing VLANs are in the VTP domain?
_______________________________________________________________________________
There are seven existing VLANs in the VTP domain: five built-in VLANs and the two VLANs that were added.
Step 6: Configure ports.
Configure the host ports for the appropriate VLANs according to the diagram.
ALS1(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/6 ALS1(config-if)# switchport mode access ALS1(config-if)# switchport access vlan 100 ALS2(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/6 ALS2(config-if)# switchport mode access ALS2(config-if)# switchport access vlan 200
Ping from the host on VLAN 100 to the host on VLAN 200. Was the ping successful? Why do you think this is the case?
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
No, the ping was not successful because the hosts are in separate VLANs. Routing needs to take place between the VLANs for this ping to be successful.
Ping from a host to the VLAN 1 management IP address of DLS1. Was the ping successful? Why do you think this is the case?
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
No, the ping was not successful because the hosts are in separate VLANs. Routing needs to take place
between the VLANs for this ping to be successful.
Step 7: Configure VLAN interfaces and enable routing.
a. On DLS1, create the Layer 3 VLAN interfaces to route between VLANs using the interface vlan vlan-id command. These are known as SVIs. You do not need to set up VLAN 1, because this was done in Step
2.
DLS1(config)# interface vlan 100 DLS1(config-if)# ip add 172.16.100.1 255.255.255.0 DLS1(config-if)# no shut DLS1(config-if)# interface vlan 200 DLS1(config-if)# ip address 172.16.200.1 255.255.255.0 DLS1(config-if)# no shutdown
b. The ip routing command is also needed to allow the switch to act as a Layer 3 device to route between these VLANs. Because the VLANs are all considered directly connected, a routing protocol is not needed at this time. DLS1(config)# ip routing
c. Verify the configuration using the show ip route command on DLS1.

Step 8: Verify inter-VLAN routing by the internal route processor.
a. Ping from the Engineering host to the Finance host. Was the ping successful this time?
__________________________________________________________________________________
If the IP addressing and default gateways are set up correctly on the hosts, the ping will be successful.
b. Telnet from one of the hosts to the VLAN 1 IP address of DLS1. Can this switch be remotely accessed
from this host?
__________________________________________________________________________________
If the IP addressing and default gateways are set up correctly on the hosts, you will be able to use Telnet from
a host into a switch on VLAN 1.
Example from the Engineering host:
C:>telnet 172.16.1.1
User Access Verification
Password: <vty-password>
DLS1>
Step 9: Examine the CEF configuration.
CEF implements an advanced IP lookup and forwarding algorithm to deliver maximum Layer 3 switching performance. CEF is less CPU-intensive than route caching. In dynamic networks, fast-switching cache entries are frequently invalidated because of routing changes. This can cause traffic to be process-switched using the routing table, instead of fast-switched using the route cache. CEF uses the Forwarding Information Base (FIB) lookup table to perform destination-based switching of IP packets.
CEF is enabled by default on the 3560 switch.
a. Use the show ip cef command to display the CEF FIB.
DLS1# show ip cef Prefix Next Hop Interface 0.0.0.0/32 receive 172.16.1.0/24 attached Vlan1 172.16.1.0/32 receive 172.16.1.1/32 receive 172.16.1.101/32 attached Vlan1 172.16.1.102/32 attached Vlan1 172.16.1.255/32 receive 172.16.100.0/24 attached Vlan100 172.16.100.0/32 receive 172.16.100.1/32 receive 172.16.100.255/32 receive 172.16.200.0/24 attached Vlan200 172.16.200.0/32 receive 172.16.200.1/32 receive 172.16.200.255/32 receive 224.0.0.0/4 drop 224.0.0.0/24 receive 255.255.255.255/32 receive
b. Use the show ip interface command to verify that CEF is enabled on an interface. The following output
shows that CEF is enabled on VLAN 100.
DLS1# show ip interface vlan 100 Vlan100 is up, line protocol is up Internet address is 172.16.100.1/24 Broadcast address is 255.255.255.255 Address determined by setup command MTU is 1500 bytes Helper address is not set Directed broadcast forwarding is disabled Outgoing access list is not set Inbound access list is not set Proxy ARP is enabled Local Proxy ARP is disabled Security level is default Split horizon is enabled ICMP redirects are always sent ICMP unreachables are always sent ICMP mask replies are never sent IP fast switching is enabled IP CEF switching is enabled IP CEF switching turbo vector IP multicast fast switching is disabled IP multicast distributed fast switching is disabled IP route-cache flags are Fast, CEF Router Discovery is disabled IP output packet accounting is disabled IP access violation accounting is disabled TCP/IP header compression is disabled RTP/IP header compression is disabled Probe proxy name replies are disabled Policy routing is disabled Network address translation is disabled WCCP Redirect outbound is disabled WCCP Redirect inbound is disabled WCCP Redirect exclude is disabled BGP Policy Mapping is disabled
c. Use the show ip cef summary command to display the CEF table summary.
DLS1# show ip cef summary IPv4 CEF is enabled for distributed and running VRF Default: 18 prefixes (18/0 fwd/non-fwd) Table id 0, 0 resets Database epoch: 1 (18 entries at this epoch)
d. The show ip cef detail command shows CEF operation in detail for the switch.
DLS1# show ip cef detail IPv4 CEF is enabled for distributed and running VRF Default: 18 prefixes (18/0 fwd/non-fwd) Table id 0, 0 resets Database epoch: 1 (18 entries at this epoch) 0.0.0.0/32, epoch 1, flags receive Special source: receive receive 172.16.1.0/24, epoch 1, flags attached, connected attached to Vlan1 172.16.1.0/32, epoch 1, flags receive receive 172.16.1.1/32, epoch 1, flags receive receive 172.16.1.101/32, epoch 1 Adj source: IP adj out of Vlan1, addr 172.16.1.101 attached to Vlan1 172.16.1.102/32, epoch 1 Adj source: IP adj out of Vlan1, addr 172.16.1.102 attached to Vlan1 172.16.1.255/32, epoch 1, flags receive receive 172.16.100.0/24, epoch 1, flags attached, connected attached to Vlan100 172.16.100.0/32, epoch 1, flags receive receive 172.16.100.1/32, epoch 1, flags receive receive 172.16.100.255/32, epoch 1, flags receive receive 172.16.200.0/24, epoch 1, flags attached, connected attached to Vlan200 172.16.200.0/32, epoch 1, flags receive receive 172.16.200.1/32, epoch 1, flags receive receive 172.16.200.255/32, epoch 1, flags receive receive 224.0.0.0/4, epoch 1 Special source: drop drop 224.0.0.0/24, epoch 1, flags receive Special source: receive receive 255.255.255.255/32, epoch 1, flags receive Special source: receive Receive
Device Configurations (Instructor version)
Switch DLS1
hostname DLS1 ! enable secret cisco ! ip routing ! interface Port-channel1 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport mode trunk ! interface Port-channel2 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport mode trunk ! interface FastEthernet0/7 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport mode trunk channel-group 1 mode desirable ! interface FastEthernet0/8 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport mode trunk channel-group 1 mode desirable ! interface FastEthernet0/9 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport mode trunk channel-group 2 mode desirable ! interface FastEthernet0/10 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport mode trunk channel-group 2 mode desirable ! interface Vlan1 ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ! interface Vlan100 ip address 172.16.100.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ! interface Vlan200 ip address 172.16.200.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ! line vty 0 4 password cisco login line vty 5 15 password cisco login !
Switch ALS1
hostname ALS1 ! enable secret cisco ! interface Port-channel1 switchport mode trunk ! interface Port-channel2 switchport mode trunk ! interface FastEthernet0/6 switchport access vlan 100 switchport mode access ! interface FastEthernet0/7 switchport mode trunk channel-group 2 mode desirable ! interface FastEthernet0/8 switchport mode trunk channel-group 2 mode desirable ! interface FastEthernet0/11 switchport mode trunk channel-group 1 mode desirable ! interface FastEthernet0/12 switchport mode trunk channel-group 1 mode desirable ! interface Vlan1 ip address 172.16.1.101 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ! ip default-gateway 172.16.1.1 ! line vty 0 4 password cisco login line vty 5 15 password cisco login ! end
Switch ALS2
hostname ALS2 ! enable secret cisco ! interface Port-channel1 switchport mode trunk ! interface Port-channel2 switchport mode trunk ! interface FastEthernet0/6 switchport access vlan 200 switchport mode access ! interface FastEthernet0/9 switchport mode trunk channel-group 2 mode desirable ! interface FastEthernet0/10 switchport mode trunk channel-group 2 mode desirable ! interface FastEthernet0/11 switchport mode trunk channel-group 1 mode desirable ! interface FastEthernet0/12 switchport mode trunk channel-group 1 mode desirable ! interface Vlan1 ip address 172.16.1.102 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ! ip default-gateway 172.16.1.1 ! line vty 0 4 password cisco login line vty 5 15 password cisco login ! end
More Resources