CCNP Switch: IP Telephony Power over Ethernet (PoE) A Cisco IP Phone is like any other node on the network—it must have power to operate. Power can come from two sources: An external AC adapter Power over Ethernet (DC) over the network data cable The external AC adapter plugs into a normal AC wall outlet and provides 48V DC to the phone. These adapters, commonly … [Read more...]
CCNP Switch: Securing Switch Access
CCNP Switch: Securing Switch Access Switch AAA You can manage user activity to and through a switch with authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) features. AAA uses standardized methods to challenge users for their credentials before access is allowed or authorized. Accounting protocols also can record user activity on a switch. Authentication Switch or network … [Read more...]
CCNP Switch: Router, Supervisor, and Power Redundancy
CCNP Switch: Router, Supervisor, and Power Redundancy Router Redundancy in Multilayer Switching Multilayer switches can act as IP gateways for connected hosts by providing gateway addresses at VLAN SVIs and Layer 3 physical interfaces. These switches can also participate in routing protocols, just as traditional routers do. For high availability, multilayer switches should … [Read more...]
CCNP Switch: Multilayer Switching
CCNP Switch: Multilayer Switching InterVLAN Routing Recall that a Layer 2 network is defined as a broadcast domain. A Layer 2 network also can exist as a VLAN inside one or more switches. VLANs essentially are isolated from each other so that packets in one VLAN cannot cross into another VLAN. To transport packets between VLANs, you must use a Layer 3 device. … [Read more...]
CCNP Switch: Protecting the Spanning Tree Protocol Topology
CCNP Switch: Protecting the Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Protecting Against Unexpected BPDUs A network running STP uses BPDUs to communicate between switches (bridges). Switches become aware of each other and of the topology that interconnects them. After a Root Bridge is elected, BPDUs are generated by the root and are relayed down through the spanning-tree topology. … [Read more...]
CCNP Switch: Securing with VLANs
CCNP Switch: Securing with VLANs VLAN Access Lists Access lists can manage or control traffic as it passes through a switch. When normal access lists are configured on a Catalyst switch, they filter traffic through the use of the Ternary Content Addressable Memory (TCAM). Recall from Chapter 3, “Switch Operation,” that access lists (also known as router access lists, or … [Read more...]
CCNP Switch: Traditional Spanning Tree Protocol
CCNP Switch: Traditional Spanning Tree Protocol IEEE 802.1D Overview A robust network design not only includes efficient transfer of packets or frames, but also considers how to recover quickly from faults in the network. In a Layer 3 environment, the routing protocols in use keep track of redundant paths to a destination network so that a secondary path can be used quickly … [Read more...]
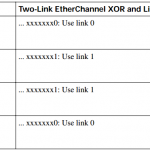
CCNP Switch: Aggregating Switch Links
CCNP Switch: Aggregating Switch Links Switch Port Aggregation with EtherChannel As discussed in Chapter 5, “Switch Port Configuration,” switches can use Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, or Gigabit Ethernet ports to scale link speeds by a factor of ten. Cisco offers another method of scaling link bandwidth by aggregating, or bundling, parallel links, termed the EtherChannel … [Read more...]
CCNP Switch: VLAN Trunking Protocol
CCNP Switch: VLAN Trunking Protocol VLAN Trunking Protocol As the previous chapter demonstrated, VLAN configuration and trunking on a switch or a small group of switches is fairly intuitive. Campus network environments, however, usually consist of many interconnected switches. Configuring and managing a large number of switches, VLANs, and VLAN trunks quickly can get out of … [Read more...]
CCNP Switch: VLANs and Trunks
CCNP Switch: VLANs and Trunks Virtual LANs Consider a network design that consists of Layer 2 devices only. For example, this design could be a single Ethernet segment, an Ethernet switch with many ports, or a network with several interconnected Ethernet switches. A full Layer 2–only switched network is referred to as a flat network topology. A flat network is a single … [Read more...]