CCNP Route FAQ: Controlling Routing Updates Across the Network
Q1. State two of the methods that Cisco recommends for controlling routing traffic.
Answer: The methods that Cisco discusses as useful methods of controlling routing updates are as follows:
- Passive interfaces: Prevent network communication and thus an adjacency from being formed with neighboring routers.
- Changing the administrative distance on the route: Changes the natural order as laid down by Cisco on which routing protocol is more plausible than the others. A scale of weighting is applied to the protocols.
- Default routes: Instruct the interface on where to send the destination traffic if the routing table had no entry for that destination.
- Static routes: Offers the ability to manually configure the path to a destination network.
- Route update filtering: Offers the use of access lists to configure.
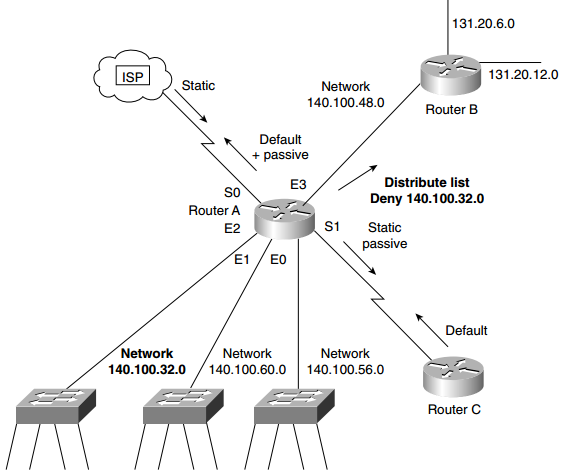
Figure: Controlling Routing Updates
Q2. What is the administrative distance for RIP?
Q3. State two instances when you do not want routing information propagated.
Answer: The two occasions that you do not want routing information to be propagated are as follows:
- If there is a WAN link where the cost of the link is based on network traffic. This may also have the added disincentive of being a WAN link that is a dial-on-demand link, which is raised and maintained by the presence of traffic attempting to flow across the interface.
- The other situation in which you should prevent routing updates from being propagated is when you are trying to prevent routing loops. If the routing domain has redundant paths that will be learned by different routing protocol, it is advisable to filter the propagation of one of the paths.
Q4. In what instances will Enhanced IGRP automatically redistribute?
Q5. Which command is used to view the administrative distance on a route?
Q6. When is redistribution required?
Q7. Why does Cisco recommend that you not overlap routing protocols?
Q8. Why would you want to prevent routing updates across an on-demand WAN link?
Q9. What is the metric used for in a routing protocol?
Q10. Explain the command match ip-address {access-list-number | name} [access-list number | name].
Access lists are used to specify the addressing of the packets to be affected.
Q11. Explain the command ip-route-cache policy.
Q12. Give two reasons for using multiple routing protocols.
Answer: The main reasons for multiple protocols existing within an organization are as follows:
- The organization is transitioning from one routing protocol to another because the network has grown and there is a need for a more sophisticated protocol that will scale.
- Although a vendor solution is preferred, there is a mix of different vendors within the network, so the vendor solution is used in the areas available. This is particularly true in client/server networks.
- Historically, the organization was a series of small network domains that have recently been tied together to form one large enterprise network. The company may well have plans to transition to a single routing protocol in the future.
- Often after a merger or a takeover, when several companies become one, it takes planning, strategy, and careful analysis to determine the best overall design for the network.
- Politically, there are ideological differences among the different network administrators, which until now have not been resolved.
- In a very large environment, the various domains may have different requirements, making a single solution inefficient. A clear example is in the case of a large multinational corporation, where EIGRP is the protocol used at the access and distribution layer, but BGP is the protocol connecting the core.
Q13. How many IP routing tables are there?
Q14. When implementing redistribution, state one possible problem that you might experience, and explain why it is a problem.
Answer: The problems experienced as a result of multiple routing processes and their redistribution include the following:
- The wrong or a less efficient routing decision being made, referred to as the suboptimal path.
- A routing loop occurring, in which the data traffic is sent in a circle without ever arriving at the destination.
- The convergence time of the network increasing because of the different technologies involved. If the routing protocols converge at different rates, this may also cause problems. In some cases, this may result in timeouts and the temporary loss of networks.
Q15. Which has a lower administrative distance, IGRP or OSPF?
Q16. What command is used to configure an outbound route filter?
distribute list {access-list-number | name} out
[ interface-name | routing process | autonomous-system number]
Q17. What is a passive interface?
Q18. What is the purpose of administrative distance?
Q19. What is the concern of redistributing into a redundant network?
Q20. What is a default network?
Q21. Why is it necessary to configure a default metric when redistributing between routing protocols?
Q22. Which command is used to modify the administrative distance of a route?
distance weight [address mask [ access-list-number | name]] [ip]
A different command is used for EIGRP and BGP-4. The EIGRP command to change the administrative distance is as follows:
distance eigrp internal-distance external-distance
Q23. What is the difference in processing for an inbound and an outbound route filter?
Q24. State two benefits of using policy-based routing.
Answer: The benefits of policy-based routing include the following:
- Organizations can determine traffic flow based on the origin of the traffic. They can send traffic owned by different groups across different paths.
- Quality of service (QoS) can be set in the IP header using the precedence or TOS bits. This allows certain traffic to be prioritized through the network.
- High-cost links can be raised on more specific criteria, which allows an efficient use of the resources available.
- Traffic can be send across multiple paths based on traffic characteristics.
Q25. How are matching routes modified in a route map?
Q26. Explain the command set ip default-next-hop [ip-address…ip-address].
Q27. Which command displays route maps that are configured on interfaces?