CCNP Route FAQ: BGP Path Control
Q1. An engineer is preparing an implementation plan in which the configuration needs to influence BGP’s choice of best path. Which of the following is least likely to be used by the configuration in this implementation plan?
a. Weight
b. Origin code
c. AS_Path
d. Local_Pref
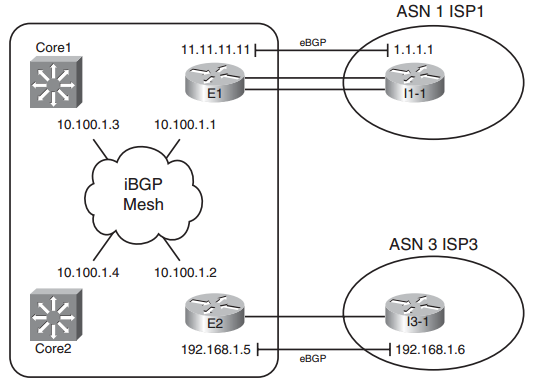
Figure: Sample Internetwork for BGP Local_Pref and AS_Path Length Examples
Q2. Router R1 learns two routes with BGP for prefix 200.1.0.0/16. Comparing the two routes, route 1 has a longer AS_Path Length, bigger MED, bigger Weight, and smaller Local Preference. Which of the following is true about Router R1’s choice of best path for this prefix?
a. Route 1 is the best route.
b. Route 2 is the best route.
c. The routes tie as best, but one will be picked to be placed in the routing table based on tiebreakers.
d. Neither route is considered best.
Q3. Router R1 learns two routes with BGP for prefix 200.1.0.0/16. Comparing the two routes, route 1 has a shorter AS_Path Length, smaller MED, the same Weight, and smaller Local Preference. Which of the following is true about Router R1’s choice of best path for this prefix?
a. Route 1 is the best route.
b. Route 2 is the best route.
c. The routes tie as best, but one will be picked to be placed in the routing table based on tiebreakers.
d. Neither route is considered best.
Q4. An engineer has been told to create an implementation plan to influence the choice of best BGP route on a single router using the Weight feature. The sole Enterprise Internet-connected router, Ent1, has neighbor relationships with Routers ISP1 and ISP2, which reside inside two different ISPs. The goal is to prefer all routes learned from ISP1 over ISP2 using Weight. Which of the following answers lists a configuration step that would not be useful for achieving these goals? (Choose two.)
a. Configuring the neighbor weight command on Ent1.
b. Having the ISPs configure the neighbor route-map out command on ISP1 and ISP2, with the route map setting weight.
c. Configuring the set weight command inside a route map on Router Ent1.
d. Configuring a prefix list to match all class C networks.
Q5. The following output on Router R1 lists details of a BGP route for 190.1.0.0/16. Which of the following is true based on this output? (Choose two.)
R1# show ip bgp 190.1.0.0/16 BGP routing table entry for 190.1.0.0/16, version 121 Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table) Advertised to update-groups: 1 1 2 3 4 1.1.1.1 from 2.2.2.2 (3.3.3.3) Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
a. R1 has a neighbor 1.1.1.1 command configured.
b. R1 has a neighbor 2.2.2.2 command configured.
c. The show ip bgp command lists a line for 190.1.0.0/16 with both an “>” and an “i” on the left.
d. R1 is in ASN 1.
Q6. An Enterprise router, Ent1, displays the following excerpt from the show ip bgp command. ENT1 has an eBGP connection to an ISP router with address 3.3.3.3 and an iBGP connection to a router with address 4.4.4.4. Which of the following is most likely to be true?
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 3.3.3.3 0 0 1 1 1 1 2 18 i
a. The Enterprise likely uses ASN 1.
b. The neighboring ISP likely uses ASN 1.
c. The route has been advertised through ASN 1 multiple times.
d. Router Ent1 will add another ASN to the AS_Path before advertising this route to its iBGP peer (4.4.4.4).
Q7. The following line of output was gathered on Enterprise Router Ent1 using the command show ip route. Which of the following answers is most likely to be true, based on this output?
B 128.107.0.0 [20/10] via 11.11.11.11, 00:02:18
a. This router has set the Weight of this route to 10.
b. This router’s BGP table lists this route as an iBGP route.
c. This router’s MED has been set to 10.
d. This router’s BGP table lists an AS_Path length of 10 for this route.