CCNA RSE 2.3 2.4 Lab – Troubleshooting Ipv4 and Ipv6 Static Routes
CCNA 2 2.3 2.4 Lab – packet tracer troubleshooting ipv4 and ipv6 addressing Static Routes Answers
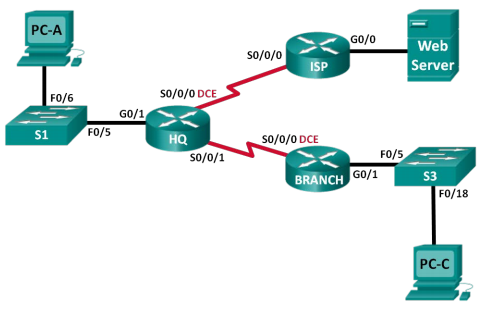
Topology
Troubleshooting Ipv4 and Ipv6 static routes Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Default Gateway |
| HQ | G0/1 | 192.168.0.1/25 2001:DB8:ACAD::1/64 FE80::1 link-local |
N/A |
| S0/0/0 (DCE) | 10.1.1.2/30 2001:DB8:ACAD::20:2/64 |
N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.0.253/30 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1/30 |
N/A | |
| ISP | G0/0 | 172.16.3.1/24 2001:DB8:ACAD:30::1/64 FE80::1 link-local |
N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 10.1.1.1/30 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::1 /64 |
N/A | |
| BRANCH | G0/1 | 192.168.1.1/24 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1/64 FE80::1 link-local |
N/A |
| S0/0/0(DCE) | 192.168.0.254/30 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::2/64 |
N/A | |
| S1 | VLAN 1 | N/A | N/A |
| S3 | VLAN 1 | N/A | N/A |
| PC-A | NIC | 192.168.0.3/25 2001:DB8:ACAD::3/64 |
192.168.0.1 FE80::1 |
| Web Server | NIC | 172.16.3.3/24 2001:DB8:ACAD:30::3/64 |
172.16.3.1 FE80::1 |
| PC-C | NIC | 192.168.1.3/24 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::3/64 |
192.168.1.1 FE80::1 |
Objectives
Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings
Part 2: Troubleshoot Static Routes in an IPv4 Network
Part 3: Troubleshoot Static Routes in an IPv6 Network
Background / Scenario
As a network administrator, you must be able to configure routing of traffic using static routes. Understanding how to configure and troubleshoot static routing is a requirement. Static routes are commonly used for stub networks and default routes. Your company’s ISP has hired you to troubleshoot connectivity issues on the network. You will have access to the HQ, BRANCH, and the ISP routers.
In this lab, you will begin by loading configuration scripts on each of the routers. These scripts contain errors that will prevent end-to-end communication across the network. You will need to troubleshoot each router to determine the configuration errors, and then use the appropriate commands to correct the configurations. When you have corrected all of the configuration errors, the hosts on the network should be able to communicate with each other.
Note: The routers used with CCNA hands-on labs are Cisco 1 941 Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) with Cisco IOS Release 1 5.2(4)M3 (universalk9 image). The switches used are Cisco Catalyst 2960s with Cisco IOS Release 1 5.0(2) (lanbasek9 image). Other routers, switches, and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of this lab for the correct interface identifiers.
Note: Make sure that the routers and switches have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure, contact your instructor.
Instructor Note: Refer to the Instructor Lab Manual for the procedures to initialize and reload devices.
Required Resources
- 3 Routers (Cisco 1941 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 universal image or comparable)
- 2 Switches (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
- 3 PCs (Windows 7, Vista, or XP with terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term)
- Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
- Ethernet and serial cables as shown in the topology
Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings
In Part 1 , you will set up the network topology and configure the routers and switches with some basic settings, such as passwords and IP addresses. Preset configurations are also provided for you for the initial router configurations. You will also configure the IP settings for the PCs in the topology.
Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Attach the devices as shown in the topology diagram and cable, as necessary.
Step 2: Initialize and reload the routers and switches.
Step 3: Configure basic settings for each router.
a. Disable DNS lookup.
b. Configure device name as shown in the topology.
c. Assign class as the privileged EXEC mode password.
d. Assign cisco as the console and vty passwords.
e. Configure logging synchronous to prevent console messages from interrupting command entry.
Step 4: Configure hosts and Web Server.
a. Configure IP addresses for IPv4 and IPv6.
b. Configure IPv4 default gateway.
Step 5: Load router configurations.
Router HQ
hostname HQ ipv6 unicast-routing interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD::1/64 ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.128 ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local ! no shutdown interface Serial0/0/0 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::2/64 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 clock rate 800000 no shutdown interface Serial0/0/1 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::3/64 !ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1/64 ip address 192.168.0.253 255.255.255.252 no shutdown ip route 172.16.3.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.1 ip route 192.168. 1.0 255.255.255.0 192.16.0.254 ! ip route 192.168. 1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.254 ipv6 route 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::/64 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::2 ipv6 route 2001:DB8:ACAD:30::/64 2001:DB8:ACAD::20: 1 !ipv6 route 2001:DB8:ACAD:30::/64 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::1
Router ISP
hostname ISP ipv6 unicast-routing interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:30::1/64 ip address 172.16.3. 11 255.255.255.0 ! ip address 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local no shutdown interface Serial0/0/0 ipv6 address 2001:DB8: : ACAD:20:1/64 !ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::1/64 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 no shutdown ip route 192.168. 1.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.2 ! ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.254.0 10.1.1.2 ipv6 route 2001:DB8:ACAD::/62 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::2
Router BRANCH
hostname BRANCH ipv6 unicast-routing interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1/64 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local no shutdown interface Serial0/0/0 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::2/64 clock rate 128000 ip address 192.168.0.249 255.255.255.252 ! ip address 192.168.0. 254 255.255.255.252 clock rate 128000 no shutdown ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.2 ! ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.253 ! ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 route ::/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:: 1 !ipv6 route ::/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1
Part 2: Troubleshoot Static Routes in an IPv4 Network
IPv4 Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
| HQ | G0/1 | 192.168.0.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 (DCE) | 10.1.1.2 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.0.253 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| ISP | G0/0 | 172.16.3.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 10.1.1.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| BRANCH | G0/1 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0(DCE) | 192.168.0.254 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| S1 | VLAN 1 | 192.168.0.11 | 255.255.255.128 | 192.168.0.1 |
| S3 | VLAN 1 | 192.168.1.11 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
| PC-A | NIC | 192.168.0.3 | 255.255.255.128 | 192.168.0.1 |
| Web Server | NIC | 172.16.3.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.16.3.1 |
| PC-C | NIC | 192.168.1.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
Step 1: Troubleshoot the HQ router.
The HQ router is the link between the ISP router and the BRANCH router. The ISP router represents the outside network while the BRANCH router represents the corporate network. The HQ router is configured with static routes to ISP and BRANCH networks.
a. Display the status of the interfaces on HQ. Enter show ip interface brief. Record and resolve any issues as necessary.
The interface g0/1 is status administratively down and protocol down. Issue the no shutdown command on interface g0/1 to resolve the issue.
HQ# show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down GigabitEthernet0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down GigabitEthernet0/1 192.168.0.1 YES manual administratively down down Serial0/0/0 10.1.1.2 YES manual up up Serial0/0/1 192.168.0.253 YES manual up up
b. Ping from HQ router to BRANCH router (192.168.0.254). Were the pings successful? ________ No
c. Ping from HQ router to ISP router (10.1.1.1). Were the pings successful? ________ Yes
d. Ping from PC-A to the default gateway. Were the pings successful? ________ Yes
e. Ping from PC-A to PC-C. Were the pings successful? ________ No
f. Ping from PC-A to Web Server. Were the pings successful? ________ No
g. Display the routing table on HQ. What non-directly connected routes are shown in the routing table?
static route to 172.16.3.0/24 via 10.1.1.1 . no route to 192.168.1.0/24
HQ# show ip route <Output omitted> Gateway of last resort is not set 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 L 10.1.1.2/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets S 172.16.3.0 [1/0] via 10.1.1.1 192.168.0.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 192.168.0.252/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 L 192.168.0.253/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
h. Based on the results of the pings, routing table output, and static routes in the running configuration, what can you conclude about network connectivity?
There is a static route to PC-C’s network but it does not show in the route table, need to re-enter route with correct destination IP. There is a static route to the 172.16.3.0 network but the Web Server is not reachable.
HQ# show run | include ip route ip route 172.16.3.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.1 ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.16.0.254
i. What commands (if any) need to be entered to resolve routing issues? Record the command(s).
HQ(config)# no ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.16.0.254 HQ(config)# ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.254
j. Repeat any of the steps from b to f to verify whether the problems have been resolved. Record your observations and possible next steps in troubleshooting connectivity.
The routing problems have not been resolved. The HQ router still cannot ping the BRANCH router. This may indicate there is an issue on BRANCH router that is preventing PC-A from pinging PC-C successfully. The HQ router can reach ISP router, but PC-A cannot ping Web Server. There may be an issue on the ISP router.
HQ# show ip route <Output omitted> Gateway of last resort is not set 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 L 10.1.1.2/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets S 172.16.3.0 [1/0] via 10.1.1.1 192.168.0.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 192.168.0.252/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 L 192.168.0.253/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 S 192.168.1.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.0.254
Step 2: Troubleshoot the ISP router.
For the ISP router, there should be a route to HQ and BRANCH routers. One static route is configured on ISP router to reach the 192.168.1.0/24, 192.168.0.0/25, and 192.168.0.252/30 networks.
a. Display the status of interfaces on ISP. Enter show IP interface brief. Record and resolve any issues as necessary.
The IP address for G0/0 is incorrectly configured.
ISP(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ISP(config-if)# ip address 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 ISP# show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down GigabitEthernet0/0 172.16.3.11 YES manual up up GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down Serial0/0/0 10.1.1.1 YES manual up up Serial0/0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
b. Ping from the ISP router to the HQ router (10.1.1.2). Were the pings successful? ________ Yes
c. Ping from Web Server to the default gateway. Were the pings successful? ________ Yes
d. Ping from Web Server to PC-A. Were the pings successful? ________ No
e. Ping from Web Server to PC-C. Were the pings successful? ________ No
f. Display the routing table on ISP. What non-directly connected routes are shown in the routing table?
A static route to 192.168.1.0/24 via 10.1.1.2 No route to 192.168.0.252/30
ISP# show ip route <Output omitted> Gateway of last resort is not set 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 L 10.1.1.1/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 172.16.3.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0 L 172.16.3.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0 S 192.168.1.0/24 [1/0] via 10.1.1.2
g. Based on the results of the pings, routing table output, and static routes in the running configuration, what can you conclude about network connectivity?
A summary route to 192.168.0.0/23 is needed to reach both 192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.0.252/30 network.
h. What commands (if any) need to be entered to resolve routing issues? Record the command(s). (Hint: ISP only requires one summarized route to the company’s networks 192.168.1.0/24, 192.168.0.0/25, and 192.168.0.252/32.)
ISP(config)# no ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.2 ISP(config)# ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.254.0 10.1.1.2
i. Repeat any of the steps from b to e to verify whether the problems have been resolved. Record your observations and possible next steps in troubleshooting connectivity.
After the correction, Web Server can reach PC-A. However, Web Server still cannot ping PC-C. There are still more unresolved issues in the network.
ISP# show ip route <Output omitted> Gateway of last resort is not set 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 L 10.1.1.1/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 172.16.3.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0 L 172.16.3.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0 S 192.168.0.0/23 [1/0] via 10.1.1.2
Step 3: Troubleshoot the BRANCH router.
For the BRANCH router, a default route is set to reach the rest of the network and ISP.
a. Display the status of the interfaces on BRANCH. Enter show ip interface brief. Record and resolve any issues, as necessary.
The IP address for S0/0/1 is incorrectly configured. BRANCH(config)# interface s0/0/0 BRANCH(config-if)# ip address 192.168.0.254 255.255.255.252 BRANCH# show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down GigabitEthernet0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down GigabitEthernet0/1 192.168.1.1 YES manual up up Serial0/0/0 192.168.0.249 YES manual up up Serial0/0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
b. Ping from the BRANCH router to the HQ router (192.168.0.253). Were the pings successful? ________ Yes
c. Ping from PC-C to the default gateway. Were the pings successful? ________ Yes
d. Ping from PC-C to PC-A. Were the pings successful? ________ No
e. Ping from PC-C to Web Server. Were the pings successful? ________ No
f. Display the routing table on BRANCH. What non-directly connected routes are shown in the routing table?
None.
BRANCH# show ip route <Output omitted> Gateway of last resort is not set 192.168.0.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 192.168.0.252/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 L 192.168.0.254/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 192.168.1.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
g. Based on the results of the pings, routing table output, and static routes in the running configuration, what can you conclude about network connectivity?
No static routes are displayed in the routing table. The default route was configured incorrectly.
BRANCH# show run | include ip route ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.2
h. What commands (if any) need to be entered to resolve routing issues? Record the command(s).
BRANCH(config)# no ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.2 BRANCH(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.253
i. Repeat any of the steps from b to e to verify whether the problems have been resolved. Record your observations and possible next steps in troubleshooting connectivity.
BRANCH# show ip route <Output omitted> Gateway of last resort is 192.168.0.253 to network 0.0.0.0 S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 192.168.0.253 192.168.0.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 192.168.0.252/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 L 192.168.0.254/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 192.168.1.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
Part 3: Troubleshoot Static Routes in an IPv6 Network
| Device | Interface | IPv6 Address | Prefix Length | Default Gateway |
| HQ | G0/1 | 2001:DB8:ACAD::1 | 64 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 (DCE) | 2001:DB8:ACAD::20:2 | 64 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1 | 64 | N/A | |
| ISP | G0/0 | 2001:DB8:ACAD:30::1 | 64 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::1 | 64 | N/A | |
| BRANCH | G0/1 | 2001:DB8:ACAD:1 ::1 | 64 | N/A |
| S0/0/0(DCE) | 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::2 | 64 | N/A | |
| PC-A | NIC | 2001:DB8:ACAD::3 | 64 | FE80::1 |
| Web Server | NIC | 2001:DB8:ACAD:30::3 | 64 | FE80::1 |
| PC-C | NIC | 2001:DB8:ACAD:1 ::3 | 64 | FE80::1 |
Step 1: Troubleshoot the HQ router.
The HQ router is the link between the ISP router and the BRANCH router. The ISP router represents the outside network while the BRANCH router represents the corporate network. The HQ router is configured with static routes to both the ISP and the BRANCH networks.
a. Display the status of the interfaces on HQ. Enter show ipv6 interface brief. Record and resolve any issues, as necessary.
The IPv6 address for S0/0/1 is incorrectly configured.
HQ(config)# interface s0/0/1 HQ(config-if)# no ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::3/64 HQ(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1/64 HQ# show ipv6 interface brief Em0/0 [administratively down/down] unassigned GigabitEthernet0/0 [administratively down/down] unassigned GigabitEthernet0/1 [up/up] FE80::1 2001:DB8:ACAD::1 Serial0/0/0 [up/up] FE80::D68C:B5FF:FECE:A0C0 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::2 Serial0/0/1 [up/up] FE80::D68C:B5FF:FECE:A0C0 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::3ping
b. Ping from the HQ router to the BRANCH router (2001:DB8:ACAD:2::2). Were the pings successful?——-Yes
c. Ping from the HQ router to the ISP router (2001 :DB8:ACAD:20::1). Were the pings successful? ________ No
d. Ping from PC-A to the default gateway. Were the pings successful? ________ Yes
e. Ping from PC-A to Web Server. Were the pings successful? ________ No
f. Ping from PC-A to PC-C. Were the pings successful? ________ No
g. Display the routing table by issuing a show ipv6 route command. What non-directly connected routes are shown in the routing table?
Static route to 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::/64 via 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::2
Static route to 2001:DB8:ACAD:30::/64 via 2001:DB8:ACAD::20:1
HQ# show ipv6 route IPv6 Routing Table - default - 9 entries <Output omitted> C 2001:DB8:ACAD::/64 [0/0] via GigabitEthernet0/1, directly connected L 2001:DB8:ACAD::1/128 [0/0] via GigabitEthernet0/1, receive S 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::/64 [1/0] via 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::2 C 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::/64 [0/0] via Serial0/0/1, directly connected L 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1/128 [0/0] via Serial0/0/1, receive C 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::/64 [0/0] via Serial0/0/0, directly connected L 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::2/128 [0/0] via Serial0/0/0, receive S 2001:DB8:ACAD:30::/64 [1/0] via 2001:DB8:ACAD::20:1 L FF00::/8 [0/0] via Null0, receive
h. Based on the results of the pings, routing table output, and static routes in the running configuration, what can you conclude about network connectivity?
Static route to 2001:DB8:ACAD:30::/64 has an incorrectly configured next hop address.
i. What commands (if any) need to be entered to resolve routing issues? Record the command(s).
HQ(config)# no ipv6 route 2001:DB8:ACAD:30::/64 2001:DB8:ACAD::20:1 HQ(config)# ipv6 route 2001:DB8:ACAD:30::/64 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::1
j. Repeat any of the steps from b to f to verify whether the problems have been resolved. Record your observations and possible next steps in troubleshooting connectivity.
The routing problems have not been resolved. The HQ router still cannot ping ISP router. The ISP router probably has IP address issue. PC-A still cannot ping PC-C and Web Server.
HQ# show ipv6 route IPv6 Routing Table - default - 9 entries <Output omitted> C 2001:DB8:ACAD::/64 [0/0] via GigabitEthernet0/1, directly connected L 2001:DB8:ACAD::1/128 [0/0] via GigabitEthernet0/1, receive S 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::/64 [1/0] via 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::2 C 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::/64 [0/0] via Serial0/0/1, directly connected L 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1/128 [0/0] via Serial0/0/1, receive C 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::/64 [0/0] via Serial0/0/0, directly connected L 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::2/128 [0/0] via Serial0/0/0, receive S 2001:DB8:ACAD:30::/64 [1/0] via 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::1 L FF00::/8 [0/0] via Null0, receive
Step 2: Troubleshoot the ISP router.
On the ISP router, one static route is configured to reach all the networks on HQ and BRANCH routers.
a. Display the status of the interfaces on ISP. Enter show ipv6 interface brief. Record and resolve any issues, as necessary.
The IPv6 address for S0/0/0 is incorrectly configured.
ISP(config)# interface s0/0/0 ISP(config-if)# no ipv6 address 2001:DB8::ACAD:20:1/64 ISP(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::1/64 ISP# show ipv6 interface brief Em0/0 [administratively down/down] unassigned GigabitEthernet0/0 [up/up] FE80::1 2001:DB8:ACAD:30::1 GigabitEthernet0/1 [administratively down/down] unassigned Serial0/0/0 [up/up] FE80::FE99:47FF:FE71:78A0 2001:DB8::ACAD:20:1 Serial0/0/1 [administratively down/down] unassigned
b. Ping from the ISP router to the HQ router (2001:DB8:ACAD:20::2). Were the pings successful? ________ Yes
c. Ping from Web Server to the default gateway. Were the pings successful? ________ Yes
d. Ping from Web Server to PC-A. Were the pings successful? ________ Yes
e. Ping from Web Server to PC-C. Were the pings successful? ________ No
f. Display the routing table. What non-directly connected routes are shown in the routing table?
Static route to 2001:DB8:ACAD::/62 via 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::2
ISP# show ipv6 route IPv6 Routing Table - default - 6 entries <Output omitted> S 2001:DB8:ACAD::/62 [1/0] via 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::2 C 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::/64 [0/0] via Serial0/0/0, directly connected L 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::1/128 [0/0] via Serial0/0/0, receive C 2001:DB8:ACAD:30::/64 [0/0] via GigabitEthernet0/0, directly connected L 2001:DB8:ACAD:30::1/128 [0/0] via GigabitEthernet0/0, receive L FF00::/8 [0/0] via Null0, receive
g. Based on the results of the pings, routing table output, and static routes in the running configuration, what can you conclude about network connectivity?
No issues with the static route
h. What commands (if any) need to be entered to resolve routing issues? Record the command(s).
None
i. Repeat any of the steps from b to e to verify whether the problems have been resolved. Record your observations and possible next steps in troubleshooting connectivity.
Not all routing issues have been resolved. Web Server still cannot ping PC-C.
Step 3: Troubleshoot the BRANCH router.
For the BRANCH routers, there is a default route to the HQ router. This default route allows the BRANCH network to the ISP router and Web Server.
a. Display the status of the interfaces on BRANCH. Enter show ipv6 interface brief. Record and resolve any issues, as necessary.
All interfaces were configured correctly according to the Addressing Table.
BRANCH# show ipv6 interface brief Em0/0 [administratively down/down] unassigned GigabitEthernet0/0 [administratively down/down] unassigned GigabitEthernet0/1 [up/up] FE80::1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1 Serial0/0/0 [up/up] FE80::FE99:47FF: FE71:7A20 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::2 Serial0/0/1 [administratively down/down] unassigned
b. Ping from the BRANCH router to the HQ router (2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1 ). Were the pings successful? ________ Yes
c. Ping from the BRANCH router to the ISP router (2001:DB8:ACAD:20::1). Were the pings successful? ________ No
d. Ping from PC-C to the default gateway. Were the pings successful? ________ Yes
e. Ping from PC-C to PC-A. Were the pings successful? ________ No
f. Ping from PC-C to Web Server. Were the pings successful? ________ No
g. Display the routing table. What non-directly connected routes are shown in the routing table?
None
BRANCH# show ipv6 route IPv6 Routing Table - default - 5 entries <Output omitted> C 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::/64 [0/0] via GigabitEthernet0/1, directly connected L 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1/128 [0/0] via GigabitEthernet0/1, receive C 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::/64 [0/0] via Serial0/0/0, directly connected L 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::2/128 [0/0] via Serial0/0/0, receive L FF00::/8 [0/0] via Null0, receive
h. Based on the results of the pings, routing table output, and static routes in the running configuration, what can you conclude about network connectivity?
No default route is displayed in the table. The next-hop address was incorrectly configured.
i. What commands (if any) need to be entered to resolve routing issues? Record the command(s).
BRANCH(config)# no ipv6 route ::/0 2001:DB8:ACAD::1 BRANCH(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1
j. Repeat any of the steps from b to f to verify whether the problems have been resolved. Record your observations and possible next steps in troubleshooting connectivity.
BRANCH# show ipv6 route IPv6 Routing Table - default - 6 entries <Output omitted> S ::/0 [1/0] via 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1 C 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::/64 [0/0] via GigabitEthernet0/1, directly connected L 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1/128 [0/0] via GigabitEthernet0/1, receive C 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::/64 [0/0] via Serial0/0/0, directly connected L 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::2/128 [0/0] via Serial0/0/0, receive L FF00::/8 [0/0] via Null0, receive
Router Interface Summary Table
|
Router Interface Summary |
||||
| Router Model | Ethernet Interface #1 | Ethernet Interface #2 | Serial Interface #1 | Serial Interface #2 |
| 1800 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) |
Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 1900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2801 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) |
Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) |
Serial 0/1 /0 (S0/1 /0) | Serial 0/1 /1 (S0/1 /1) |
| 2811 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) |
Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0(S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface. | ||||
Device Configs
Router HQ (Corrected)
HQ# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1652 bytes ! version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname HQ ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model memory-size iomem 15 ! ! ip cef ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 cef multilink bundle-name authenticated ! interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.128 duplex auto speed auto ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD::1/64 ! interface Serial0/0/0 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::2/64 clock rate 2000000 ! interface Serial0/0/1 ip address 192.168.0.253 255.255.255.252 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1/64 ! ip forward-protocol nd ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ip route 172.16.3.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.1 ip route 192.168. 1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.254 ! ipv6 route 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::/64 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::2 ipv6 route 2001:DB8:ACAD:30::/64 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::1 ! control-plane ! line con 0 password cisco logging synchronous line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password cisco login transport input all ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 !e nd
Router ISP (Corrected)
ISP# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1493 bytes ! version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname ISP ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model memory-size iomem 15 ! ip cef ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 cef multilink bundle-name authenticated ! interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ipv6 address Fe80::1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:30::1/64 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial0/0/0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::1/64 ! interface Serial0/0/1 no ip address shutdown clock rate 2000000 ! ip forward-protocol nd ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.254.0 10.1.1.2 ! ipv6 route 2001:DB8:ACAD::/62 2001:DB8:ACAD:20::2 ! control-plane ! line con 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password cisco login transport input all ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 !e nd
Router BRANCH (Corrected)
BRANCH# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1522 bytes ! version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname BRANCH ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model memory-size iomem 10 ! ip cef ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 cef multilink bundle-name authenticated ! interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1/64 ! interface Serial0/0/0 ip address 192.168.0.254 255.255.255.252 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::2/64 clock rate 128000 ! interface Serial0/0/1 no ip address shutdown ! ip forward-protocol nd ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.253 ! ipv6 route ::/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1 ! control-plane ! line con 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password cisco login transport input all ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ! end
More Resources