CCNA Data Center FAQ: Fundamentals of IP Version 6
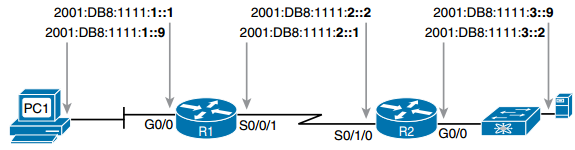
Figure: Example of Static IPv6 Addresses
Q1. Of the following list of motivations for the Internet community to create IPv6 to replace IPv4, which was the most important reason?
a. To remove the requirement to use NAT when connecting to the Internet
b. To simplify the IP header to simplify router-forwarding CPU time
c. To improve support to allow mobile devices to move into a network
d. To provide more addresses to relieve the address-exhaustion problem
Q2. Which of the following is the shortest valid abbreviation for FE80:0000:0000:0100:0000:0000:0000:0123?
a. FE80::100::123
b. FE8::1::123
c. FE80::100:0:0:0:123:4567
d. FE80:0:0:100::123
Q3. Which of the following is the shortest valid abbreviation for 2000:0300:0040:0005:6000:0700:0080:0009?
a. 2:3:4:5:6:7:8:9
b. 2000:300:40:5:6000:700:80:9
c. 2000:300:4:5:6000:700:8:9
d. 2000:3:4:5:6:7:8:9
Q4. Which of the following is the prefix for address 2000:0000:0000:0005:6000:0700:0080:0009, assuming a mask of /64?
a. 2000::5::/64
b. 2000::5:0:0:0:0/64
c. 2000:0:0:5::/64
d. 2000:0:0:5:0:0:0:0/64
Q5. Which of the following IPv6 addresses appears to be a global unicast address, based on its first few hex digits?
a. 3123:1:3:5::1
b. FE80::1234:56FF:FE78:9ABC
c. FDAD::1
d. FF00::5
Q6. When subnetting an IPv6 address block, an engineer shows a drawing that breaks the address structure into three pieces. Comparing this concept to a three-part IPv4 address structure, which part of the IPv6 address structure is most like the IPv4 network part of the address?
a. Subnet
b. Interface ID
c. Network
d. Global routing prefix
e. Subnet router anycast
Q7. When subnetting an IPv6 address block, an engineer shows a drawing that breaks the address structure into three pieces. Assuming that all subnets use the same prefix length, which of the following answers lists the name of the field on the far right side of the address?
a. Subnet
b. Interface ID
c. Network
d. Global routing prefix
e. Subnet router anycast
Q8. Host PC1 dynamically learns its IPv6 settings using stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC). Think about the host’s unicast address as two parts: the prefix and the interface ID. Which of the answers list a way that SLAAC learns or builds the value of the interface ID portion of the host’s address? (Choose two answers.)
a. Learned from a DHCPv6 server
b. Built by the host using EUI-64 rules
c. Learned from a router using NDP RS/RA messages
d. Built by the host using a random value