CCNA Data Center FAQ: Fundamentals of Ethernet LANs
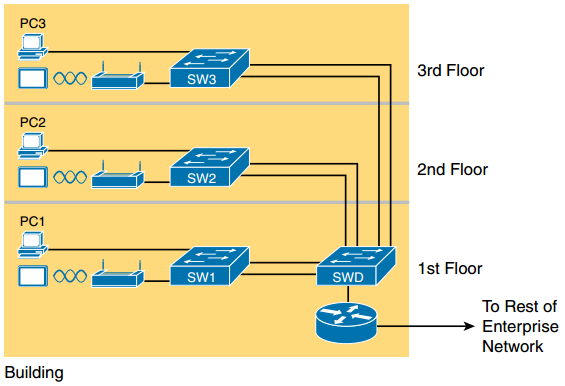 Figure: Single-Building Enterprise Wired and Wireless LAN
Figure: Single-Building Enterprise Wired and Wireless LAN
Q1. In the LAN for a small office, some user devices connect to the LAN using a cable, while others connect using wireless technology (and no cable). Which of the following is true regarding the use of Ethernet in this LAN?
a. Only the devices that use cables are using Ethernet.
b. Only the devices that use wireless are using Ethernet.
c. Both the devices using cables and those using wireless are using Ethernet.
d. None of the devices are using Ethernet.
Q2. Which of the following Ethernet standards defines Gigabit Ethernet over UTP cabling?
a. 10GBASE-T.
b. 100BASE-T.
c. 1000BASE-T.
d. None of the other answers is correct.
Q3. Which of the following is true about Ethernet crossover cables for Fast Ethernet?
a. Pins 1 and 2 are reversed on the other end of the cable.
b. Pins 1 and 2 on one end of the cable connect to pins 3 and 6 on the other end of the cable.
c. Pins 1 and 2 on one end of the cable connect to pins 3 and 4 on the other end of the cable.
d. The cable can be up to 1000 meters long to cross over between buildings.
e. None of the other answers is correct.
Q4. Each answer lists two types of devices used in a 100BASE-T network. If these devices were connected with UTP Ethernet cables, which pairs of devices would require a straight-through cable? (Choose three answers.)
a. PC and router
b. PC and switch
c. Hub and switch
d. Router and hub
e. Wireless access point (Ethernet port) and switch
Q5. Which of the following is true about the CSMA/CD algorithm?
a. The algorithm never allows collisions to occur.
b. Collisions can happen, but the algorithm defines how the computers should notice a collision and how to recover.
c. The algorithm works with only two devices on the same Ethernet.
d. None of the other answers is correct.
Q6. Which of the following is true about the Ethernet FCS field?
a. Ethernet uses FCS for error recovery.
b. It is 2 bytes long.
c. It resides in the Ethernet trailer, not the Ethernet header.
d. It is used for encryption.
Q7. Which of the following are true about the format of Ethernet addresses? (Choose three answers.)
a. Each manufacturer puts a unique OUI code into the first 2 bytes of the address.
b. Each manufacturer puts a unique OUI code into the first 3 bytes of the address.
c. Each manufacturer puts a unique OUI code into the first half of the address.
d. The part of the address that holds this manufacturer’s code is called the MAC.
e. The part of the address that holds this manufacturer’s code is called the OUI.
f. The part of the address that holds this manufacturer’s code has no specific name.
Q8. Which of the following terms describe Ethernet addresses that can be used to send one frame that is delivered to multiple devices on the LAN? (Choose two answers.)
a. Burned-in address
b. Unicast address
c. Broadcast address
d. Multicast address