CCNA DC FAQ: Anayzing Classful IPv4 Networks
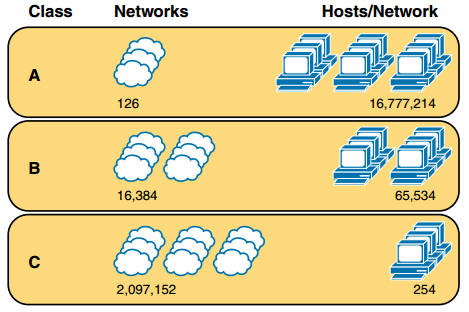
Figure: Numbers and Sizes of Class A, B, and C Networks
Q1. Which of the following are not valid Class A network IDs? (Choose two answers.)
a. 1.0.0.0
b. 130.0.0.0
c. 127.0.0.0
d. 9.0.0.0
Q2. Which of the following are not valid Class B network IDs?
a. 130.0.0.0.
b. 191.255.0.0.
c. 128.0.0.0.
d. 150.255.0.0.
e. All are valid Class B network IDs.
Q3. Which of the following are true about IP address 172.16.99.45’s IP network? (Select two answers.)
a. The network ID is 172.0.0.0.
b. The network is a Class B network.
c. The default mask for the network is 255.255.255.0.
d. The number of host bits in the unsubnetted network is 16.
Q4. Which of the following are true about IP address 192.168.6.7’s IP network? (Select two answers.)
a. The network ID is 192.168.6.0.
b. The network is a Class B network.
c. The default mask for the network is 255.255.255.0.
d. The number of host bits in the unsubnetted network is 16.
Q5. Which of the following is a network broadcast address?
a. 10.1.255.255
b. 192.168.255.1
c. 224.1.1.255
d. 172.30.255.255
Q6. Which of the following is a Class A, B, or C network ID?
a. 10.1.0.0
b. 192.168.1.0
c. 127.0.0.0
d. 172.20.0.1