CCIE SP MPLS FAQ: Carrier’s Carrier and Inter-provider VPN Solutions
Q1. Which architecture can you use to reduce the overhead on PE routers for VPN clients that want to exchange large amounts of routing information between their sites?
Q2. How does the carrier’s carrier architecture interface to the VPN client site?
Q3. What types of routes are exchanged between the MPLS VPN provider and the VPN client when using the carrier’s carrier architecture?
Q4. What types of routes are exchanged directly between VPN sites when using the carrier’s carrier architecture?
Q5. When using the carrier’s carrier, can the VPN sites run only IP with no MPLS deployed locally?
Q6. Describe the term hierarchical VPNs.
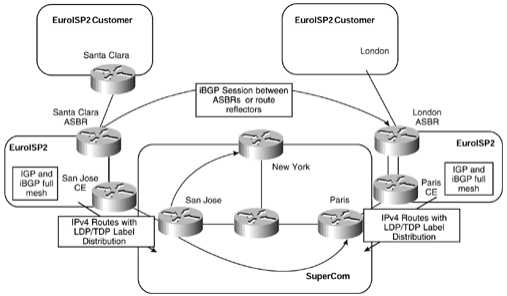
Q7. What is the purpose of the interprovider VPN solution?
Q8. How is the exchange of VPNv4 prefix information between service providers achieved?
Q9. When advertising a route from one PE-ASBR to another PE-ASBR, why does the advertising router allocate a new label?
More Resources