CCIE SP MPLS FAQ: Advanced MPLS/VPN Topics
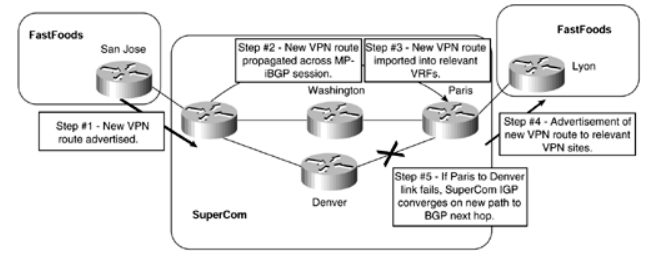
Figure: VPN and Backbone Network Convergence
1: During periods of convergence, why does a cell-mode MPLS implementation typically take longer to converge than a frame-mode implementation?
Answer: Cell-mode MPLS uses downstream-on-demand label distribution with conservative retention mode This means that an upstream
2: How often does the import scanner run on a PE router?
Answer: Frequency is based on a timer, which is 15 seconds, by default.
3: Why is it necessary to be careful when adjusting the scanner interval from its default of 60 seconds?
Answer: If there are many routes and a low scanner interval, the router’s CPU can be adversely affected.
4: Can a single BGP session carry routes for multiple address families?
Answer: Yes. In the case of MPLS VPN, this might be the IPv4 address family for Internet and the VPNv4 address family for VPN.
5: If only VPNv4 routes must be carried across a BGP session, which command prevents the advertisement of IPv4 routes?
Answer: The no bgp default ipv4-unicast command.
6: Describe the functionality of a route reflector.
Answer: The route reflector is a BGP-speaking router that propagates internal BGP routes to other internal BGP peers.
7: Describe the main benefit of route-reflector partitioning.
Answer: It allows the network to be split so that a certain set of PE routers can peer with a certain route reflector, or set of route reflectors. This setup has the advantage of helping to scale the BGP topology.
8: Describe the ORF capability.
Answer: ORF enables a router to push its inbound route filtering to a peer so that it can set its outbound route filtering to prevent the propagation of unwanted routing information.
More Resources