CCNP Route FAQ: IP Routing Principles
Q1. Name one routing protocol that sends periodic updates.
Q2. What is an incremental update, and how often is it sent out?
Q3. What is the routing algorithm used in OSPF?
Q4. State one method by which a link-state routing protocol attempts to reduce the network overhead.
Q5. Distance vector routing protocols naturally summarize at which boundary?
Q6. Which routing protocol technology uses the Bellman Ford algorithm?
Q7. Give three reasons why RIPv1 has problems with working in a large network.
Answer: RIPv1 has problems working in a large network because of the following reasons:
- It has a maximum hop count of 15.
- It sends updates of its routing table out of every interface every 30 seconds, which increases the network overhead on a network and leads to link congestion.
- To avoid routing loops, it uses holddown and poison reverse, and thereby increases the time that it takes to propagate the changes in the network.
Q8. What is the Dijkstra algorithm used for?
Q9. What is the destination address of the distance vector periodic update?
Q10. State one major difference between a classful and classless routing protocol.
Answer: Major differences between a classful and classless routing protocol include these:
- The capability to use VLSM
- The capability to summarize
- The capability to maximize the logical address space
Q11. In the routing table, a field indicates the source of the routing information. If the field showed the letter C, what would this mean?
Q12. In the routing table, how is the next logical hop indicated?
Q13. Cisco distinguishes between the routing and the switching function—what is the difference?
Q14. State the two ways that an outgoing interface is selected as the preferred path.
Answer: An outgoing interface is selected for the following reasons:
- Because it is the only available path
- Because the administrative distance is lower
- Because the metric is lower
Q15. What is administrative distance?
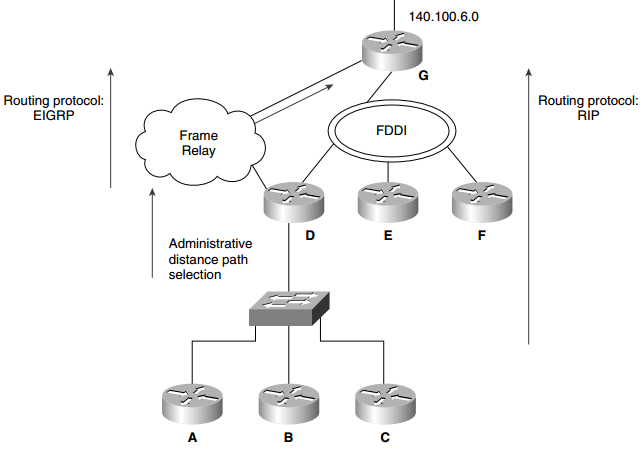
Figure: Path Selection Using Administrative Distance
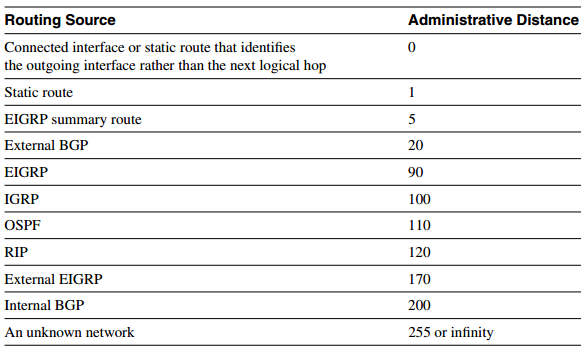
Table: Default Administrative Distance
Q16. If IGRP has three paths to a remote network in which each path has an equal metric, what will happen?
Q17. Name the interior IP routing protocols that send the mask with the routing update.
Q18. Name the interior routing protocol that sends a routing update on a Cisco router every 30 seconds by default.
Q19. Does VLSM require a classful or classless routing protocol, and why?
Q20. State one of the characteristics of a classful routing protocol.
Answer: The characteristics of a classful routing protocol are as follows:
- It summarizes at the network boundary.
- Routes exchanged between foreign networks are summarized to the NIC number.
- Within the same network (NIC number), subnet routes are exchanged by routers.
- All the interfaces on all the routers within a NIC number must share the same subnet mask.
- VLSM is not possible within the network.
Q21. A distance vector routing protocol uses the mechanism of poison reverse—what is this?
Q22. Name two distance vector routing protocols.
Q23. Name two link-state IP routing protocols.
Q24. Describe the mechanism of split horizon.
Q25. What is the command syntax to empty the Cisco routing table of all its routes?
clear ip route *
(This command must be executed from the privileged EXEC level.)
Q26. What does 0.0.0.0 signify in an IP routing table?
Q27. What is the command to show whether a specific network, such as 141.131.6.16, is present in the routing table?
show ip route 141.131.6.16
Q28. What is the next logical hop in the routing table?