CCNP Route FAQ: EIGRP Topology, Routes, and Convergence
Q1. Which of the following are methods EIGRP uses to initially populate (seed) its EIGRP topology table, before learning topology data from neighbors? (Choose two.)
a. By adding all subnets listed by the show ip route connected command
b. By adding the subnets of working interfaces over which static neighbors have been defined
c. By adding subnets redistributed on the local router from another routing source
d. By adding all subnets listed by the show ip route static command
Q2. Which of the following are both advertised by EIGRP in the Update message and included in the formula for calculating the integer EIGRP metric? (Choose two.)
a. Jitter
b. Delay
c. MTU
d. Reliability
Q3. Router R1 uses S0/0 to connect via a T/1 to the Frame Relay service. Five PVCs terminate on the serial link. Three PVCs (101, 102, and 103) are configured on subinterface S0/0.1, and one each (104 and 105) are on S0/0.2 and S0/0.3. The configuration shows no configuration related to EIGRP WAN bandwidth control, and the bandwidth command is not configured at all. Which of the following is true about how IOS tries to limit EIGRP’s use of bandwidth on S0/0?
a. R1 limits EIGRP to around 250Kbps on DLCI 102.
b. R1 limits EIGRP to around 250Kbps on DLCI 104.
c. R1 limits EIGRP to around 150Kbps on every DLCI.
d. R1 does not limit EIGRP because no WAN bandwidth control has been configured.
Q4. The output of show ip eigrp topology on Router R1 shows the following output, which is all the output related to subnet 10.11.1.0/24. How many feasible successor routes does R1 have for 10.11.1.0/24?
P 10.11.1.0/24, 2 successors, FD is 2172419
via 10.1.1.2 (2172423/28167), Serial0/0/0.1
via 10.1.1.6 (2172423/28167), Serial0/0/0.2
a. 0
b. 1
c. 2
d. 3
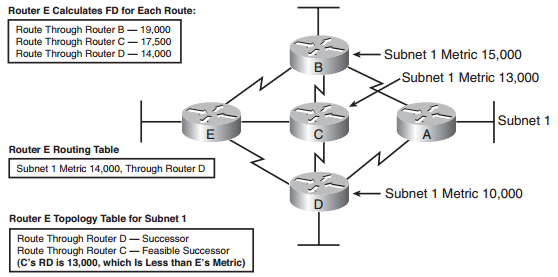
Figure: Successors and Feasible Successors with EIGRP
Q5. A network design shows that R1 has four different possible paths from itself to the Data Center subnets. Which of the following can influence which of those routes become feasible successor routes, assuming that you follow the Cisco recommended practice of not changing metric weights? (Choose two.)
a. The configuration of EIGRP offset lists
b. Current link loads
c. Changing interface delay settings
d. Configuration of variance
Q6. Router R1 is three router hops away from subnet 10.1.1.0/24. According to various show interfaces commands, all three links between R1 and 10.1.1.0/24 use the following settings: bandwidth: 1000, 500, 100000 and delay: 12000, 8000, 100. Which of the following answers correctly identifies a value that feeds into the EIGRP metric calculation? (Choose two correct answers.)
a. Bandwidth of 101,500
b. Bandwidth of about 34,000
c. Bandwidth of 500
d. Delay of 1200
e. Delay of 2010
f. Delay of 20100
Q7. Routers R1 and R2 are EIGRP neighbors. R1 has been configured with the eigrp stub connected command. Which of the following is true as a result? (Choose two correct answers.)
a. R1 can learn EIGRP routes from R2, but R2 cannot learn EIGRP routes from R1.
b. R1 can send IP packets to R2, but R2 cannot send IP packets to R1.
c. R2 no longer learns EIGRP routes from R1 for routes not connected to R1.
d. R1 no longer replies to R2’s Query messages.
e. R2 no longer sends to R1 Query messages.
Q8. A network design shows that R1 has four different possible paths from itself to the Data Center subnets. Which one of the following commands is most likely to show you all the possible next-hop IP addresses for these four possible routes?
a. show ip eigrp topology
b. show ip eigrp topology all-links
c. show ip route eigrp
d. show ip route eigrp all-links
e. show ip eigrp topology all-learned
Q9. Router R1 lists 4 routes for subnet 10.1.1.0/24 in the output of the show ip eigrp topology all-links command. The variance 200 command is configured, but no other related commands are configured. Which of the following rules are true regarding R1’s decision of what routes to add to the IP routing table? Note that RD refers to reported distance and FD to feasible distance.
a. Adds all routes for which the metric is <= 200 * the best metric among all routes
b. Adds all routes because of the ridiculously high variance setting
c. Adds all successor and feasible successor routes
d. Adds all successor and feasible successor routes for which the metric is <= 200 * the best metric among all routes