https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nhdw92ujHzU
CSMA/CD is a legacy protocol that used to be used when network shared one big collision domain. Carrier sense multiple access collision detect (CSMA/CD) describes the Ethernet access method.
CSMA/CD follows rules similar to those in a meeting. In a meeting, all individuals have the right to speak. The unspoken rule that all follows, though, is “Only one person can talk at a time.”
If you have something to say, you need to listen to see if someone is speaking. If someone is already speaking, you must wait until they are finished.
When you start to speak, you need to continue to listen in case someone else decides to speak at the same time. If this happens, both parties must stop talking and wait a random amount of time. Only then do they have the right to start the process again.
If individuals fail to observe the protocol of only one speaker at a time, the meeting quickly degenerates and no effective communication occurs.
Now with the advent of modern day switches this is not as much of a concern anymore. It is still kept in place today in order to facilitate half duplex Ethernet.
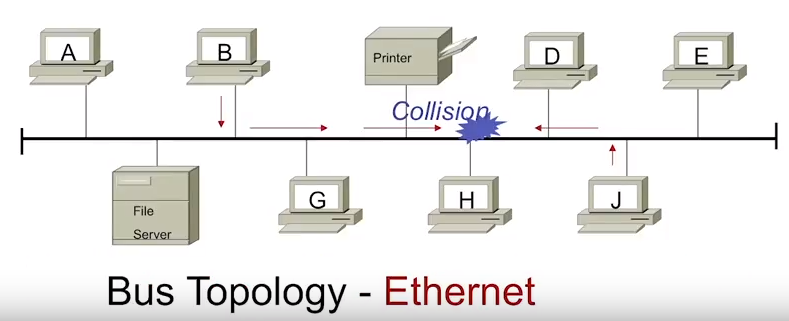
CSMA/CD or carrier sense multiple access collision detection is a way for network hosts to avoid collisions on the same collision domain.
CSMA/CD: Here’s how it works:
Carrier Sense:
Before an Ethernet device sends a frame on an Ethernet cable, it listens to find out if there is another device already transmitting a frame. That’s the carrier
sense part.
Multiple Access:
Once the device finds that the other devices are not transmitting any frame,
it starts transmitting the frame. So, what happens when two data transmissions are sent at the same time. If two devices detect that an Ethernet cable is free at the same, time then both will start transmitting the frames.
Collision Detection:
This will result in a collision. The Ethernet devices while transmitting the frames also listen for the collision. That’s the collision detected part. if they detect a collision both devices stop sending the frame and back off.
In this case we detected the collision and then we’ll send a jam signal to back off. The device then waits a logarithmic time out period and then the process is repeated until the frame is transmitted successfully for a maximum of 16 times. The frame is discarded after the sixteenth retry.