This article provides information on Graceful Routing Engine Switchover (GRES) and Nonstop Active Routing (NSR) support for Junos Subscriber Management functionalities.
How should an MX operating in a Subscriber Management environment be configured to maintain High Availability (HA)?
What is needed to perform a Unified In Service Software Upgrade (Unified ISSU)?
What role does Periodic Packet Management play in HA?
To configure an MX for HA, two protocols need to be configured, Graceful Routing Engine Switchover and Nonstop Active Routing.
Graceful Routing Engine Switchover (GRES) enables a routing platform with redundant Routing Engines (REs) to continue forwarding packets even if one RE fails. GRES preserves interface and kernel information so that traffic forwarding is not interrupted. However, GRES does not preserve control plane information so neighboring routers detect that the router has experienced a restart and react to the event in a manner prescribed by individual routing protocol specifications. To preserve routing during a switchover, GRES must be combined with either Graceful Restart protocol extensions or Nonstop Active Routing (NSR).
NSR enables a routing platform with redundant REs to switch from the primary to the backup without alerting peer nodes that a change has occurred. NSR uses the same infrastructure as GRES to preserve interface and kernel information. However, NSR also preserves routing information and protocol sessions by running the routing protocol process (rpd) on both Routing Engines. In addition, NSR preserves TCP connections maintained in the kernel. In order to use NSR, GRES must also be configured.
With GRES and NSR, the router can be upgraded via a Unified ISSU. Unified ISSU enables the system to be upgraded to a new release of Junos OS with no disruption in the control plane and minimal disruption of traffic. Unified ISSU is only supported on a system with dual REs.
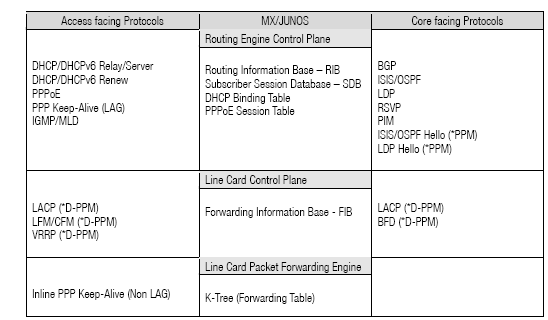
This table shows the Protocol and Local Databases that run in Junos:
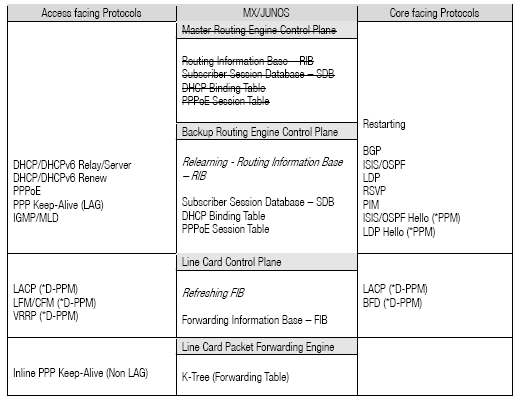
An important element to maintaining state for HA is Periodic Packet Management (PPM), referenced by ‘*PPM above’. PPM is responsible for periodic transmission and receipt of packets on behalf of its various client processes, such as Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD). By default, PPM handles time-sensitive periodic processing and performs the tasks of gathering statistics and sending process-specific packets. Distributing PPM (D-PPM) to the Packet Forwarding Engine allows the system to run time sensitive protocols like BFD on the Packet Forwarding Engine.
The following is a list of the types of sessions supported by PPM:
- BFD single-hop session for both IPv4 and IPv6, including EBGP, ISIS, and OSPF.
- Connectivity fault management (CFM) sessions.
- Link fault management (LFM) sessions.
- Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) interface sessions.
- Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) sessions.
These protocol sessions are not supported by PPM:
- BFD over an aggregated interface for IPv4, IPv6, RSTP, MSTP, and LACP.
- BFD over an IPv6 interface that does not have the global IPv6 address (or only has a link local address).
- Multihop BFD with IBGP, static routes, EBGP multihop, and MPLS LSP.
- BFD over an MPLS path using OAM.
With GRES, the Routing Information Base (RIB) is relearned and refreshed onto the newly active Master RE if there is a switch. How individual protocols and their daemons react to a GRES event differs. Most Subscriber Management daemons will have their state preserved, while most Routing Protocols will restart. The following table shows a breakdown of the GRES support:
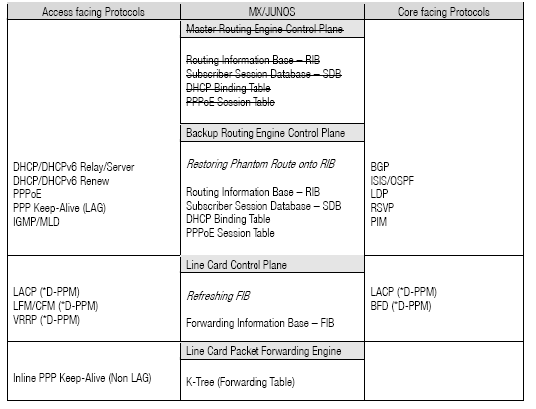
Conversely, with NSR the RIB is actively mirrored to the backup RE. Thus, there is no need for data to be learned again and protocols are not restarted. Here is the same protocol breakout referenced above for NSR:
To run NSR, the following configuration parameters are recommended to be set:
set chassis network-services enhanced-ip
Setting the network services knob to enhanced-ip forces the chassis to power on only Trio cards. The effect is that the chassis supports the greater scaling that Trio cards can support. The areas of improved scaling include routes, statistics, and filters. Without this parameter set, subscriber scaling is significantly reduced.
set accounting-options periodic-refresh disable
Periodic-refresh is disabled to change the default behavior for statistics collection. Before Broadband Edge (BBE), statistics were constantly collected by Junos. This consumes CPU cycles that are needed by BBE for call setup. So, an option to only collect statistics on demand was needed. Disabling periodic refresh makes the change in statistics collection to on demand. There is no negative impact to statistics accuracy or rate when set this way.
set system services subscriber-management gres-route-flush-delay
For a subscriber network configured with either NSR or GRES, configure the router to wait 180 seconds (3 minutes) before removing (flushing) static or dynamic access routes and access-internal routes from the forwarding table after a switch has taken place.
set system commit synchronize
Synchronize commit on both Routing Engines.
set chassis redundancy graceful-switchover
Enables graceful switchover.
set routing-options ppm redistribution-timer 120 (hidden)
This sets the time to wait after a switchover before starting PPM timers.
set routing-options nonstop-routing
Enable nonstop routing.
set routing-options nsr-phantom-holdtime 900 (hidden)
This command sets the NSR phantom route hold time.
set routing-options forwarding-table remnant-holdtime 900 (hidden)
This sets the time to hold inherited routes from the FIB.
Note: Phantom routes are used by protocols on the standby Routing Daemon that runs in NSR mode on the Backup RE to park Target Specific Information data on a prefix.
set interfaces <ae> aggregated-ether-options lacp active
This setting initiates transmission of LACP packets.
set interfaces <ae> aggregated-ether-options lacp periodic fast
This sets the interval for periodic transmission of LACP packets. Fast indicates packets are transmitted every second.
Note: Do NOT set LACP centralized. Distributed is the default.
Shown below is a summary of the parameters discussed above that have been proven to function for NSR at High Subscriber Management Scale:
system {
services {
subscriber-management {
gres-route-flush-delay;
}
}
commit {
synchronize;
}
}
chassis {
redundancy {
graceful-switchover;
}
network-services enhanced-ip;
}
routing-options {
ppm {
redistribution-timer 120;
}
nonstop-routing;
nsr-phantom-holdtime 900;
forwarding-table {
remnant-holdtime 900;
}
}
accounting-options {
periodic-refresh disable;
}
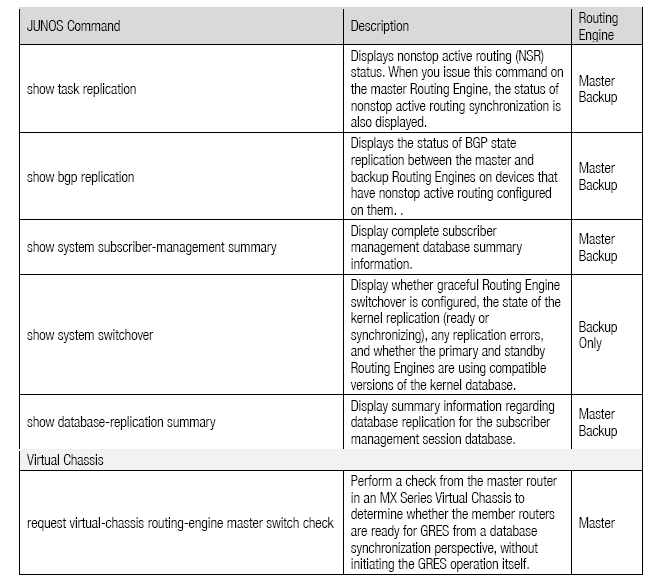
To verify that NSR is active and working correctly, the following commands can be used on the two REs in the system:
Sample Output for NSR Verification Commands:
show task replication / Master RE
poc@fulmar> show task replication
Stateful Replication: Enabled
RE mode: Master
Protocol Synchronization Status
OSPF Complete
BGP Complete
MPLS Complete
RSVP Complete
LDP Complete
show task replication / Backup RE
poc@fulmar1> show task replication
Stateful Replication: Enabled
RE mode: Backup
show bgp replication / Master RE
poc@fulmar> show bgp replication
Synchronization master:
Session state: Up, Since: 29:04
Flaps: 1, Last flap reason: Commit-sync error
Protocol state: Idle, Since: 29:04
Synchronization state: Complete
Number of peers waiting: AckWait: 0, SoWait: 0, Scheduled: 0
Messages sent: Open 1, Establish 2, Update 0, Error 0, Complete 1
Messages received: Open 1, Request 1 wildcard 0 targeted, EstablishAck 0, CompleteAck 1
{MASTER.EN_US}
show bgp replication / Backup RE
poc@fulmar1> show bgp replication
Synchronization backup:
State: Established 29:27 ago
{BACKUP.EN_US}
show system subscriber-management summary / Master RE
poc@fulmar> show system subscriber-management summary
General:
Graceful Restart Enabled
Mastership Master
Database Available
Chassisd ISSU State IDLE
ISSU State IDLE
ISSU Wait 0
{MASTER.EN_US}
show system subscriber-management summary / Backup RE
poc@fulmar1> show system subscriber-management summary
General:
Graceful Restart Enabled
Mastership Standby
Database Available
{BACKUP.EN_US}
show system switchover / Backup RE
poc@fulmar1> show system switchover
Graceful switchover: On
Configuration database: Ready
Kernel database: Ready
Peer state: Steady State
{BACKUP.EN_US}
show database-replication summary / Master RE
poc@fulmar> show database-replication summary
General:
Graceful Restart Enabled
Mastership Master
Connection Up
Database Synchronized
Message Queue Ready
{MASTER.EN_US}
show database-replication summary / Backup RE
poc@fulmar1> show database-replication summary
General:
Graceful Restart Enabled
Mastership Standby
Connection Up
Database Synchronized
Message Queue Ready
{BACKUP.EN_US}
request virtual-chassis routing-engine master switch check / Master RE
{master:member0-re0}
user@host> request virtual-chassis routing-engine master switch check
error: chassisd Not ready for mastership switch, try after 217 secs.
mastership switch request NOT honored, backup not ready