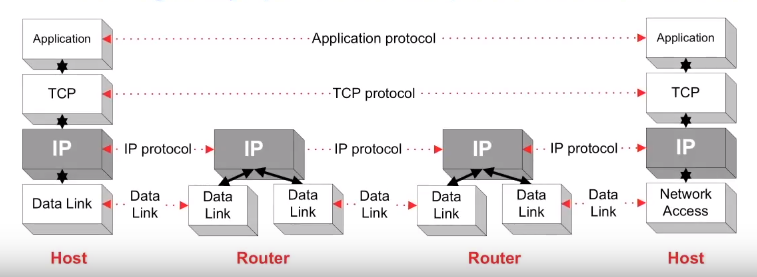
The IP protocol or internet protocol is the principal communications protocol in the Internet Protocol suite. It’s used for relaying datagrams across network boundaries. Its routing function enables internetworking and essentially establishes the internet.
IP is the primary protocol in the internet layer of the Internet Protocol suite has the task of delivering packets from the source host to the destination host solely based on the IP address in the packet headers.
As you can see IP is the highest layer protocol which is implemented on both routers and hosts. The delivery service associated with IP is minimal.
IP provides an unreliable, connectionless, best effort service also called Datagram service.
- Unreliable: IP does not make an attempt to recover lost packets.
- Connectionless: Each packet is handled independently IP is not aware that packets between hosts may not be sent in logical Sequence.
- Best-effort: IP does not make guarantees on the service (no throughput guarantee, no delay guarantee)
The consequences of this is that higher-level protocols have to deal with losses or duplicate packets and packets may be delivered out of sequence.
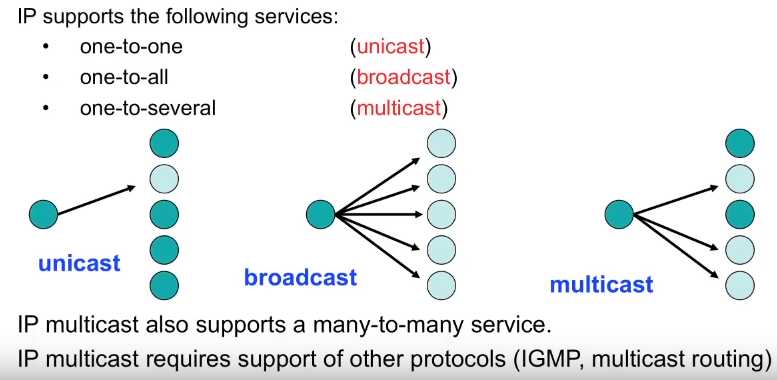
IP supports the following services
- one-to-one communication or unicast
- communication 1 – all communication or broadcast communication
- 1 to several communication or multicast communication
That being said IP multicast requires the support of other protocols such as IGMP or multicast routing.
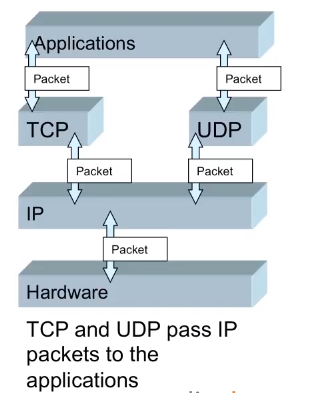
As I mentioned before IP is unreliable and connection less. It relies on higher-level protocols such as TCP and UDP to ensure packets have no errors and that all packets arrive and are correctly reassembled.
Out of the two protocols that are used, the first one is UDP.
- UDP provides unreliable connectionless delivery servicing the Internet Protocol.
- Application programs utilizing UDP accept full responsibility for packet reliability including message loss delay and out of sequence packets
With transmission control protocol or TCP
- TCP provides a reliable connection-oriented service using the Internet Protocol
- It provides reliable packet delivery, packet sequencing, error control and multiplexing