CCNP Switch FAQ : Enterprise Campus Network Design
1. Where does a collision domain exist in a switched network?
a. On a single switch port
b. Across all switch ports
c. On a single VLAN
d. Across all VLANs
2. Where does a broadcast domain exist in a switched network?
a. On a single switch port
b. Across all switch ports
c. On a single VLAN
d. Across all VLANs
3. What is a VLAN primarily used for?
a. To segment a collision domain
b. To segment a broadcast domain
c. To segment an autonomous system
d. To segment a spanning-tree domain
4. How many layers are recommended in the hierarchical campus network design model?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
e. 7
5. What is the purpose of breaking a campus network into a hierarchical design?
a. To facilitate documentation
b. To follow political or organizational policies
c. To make the network predictable and scalable
d. To make the network more redundant and secure
6. End-user PCs should be connected into which of the following hierarchical layers?
a. Distribution layer
b. Common layer
c. Access layer
d. Core layer
7. In which OSI layer should devices in the distribution layer typically operate?
a. Layer 1
b. Layer 2
c. Layer 3
d. Layer 4
8. A hierarchical network’s distribution layer aggregates which of the following?
a. Core switches
b. Broadcast domains
c. Routing updates
d. Access layer switches
9. In the core layer of a hierarchical network, which of the following are aggregated?
a. Routing tables
b. Packet filters
c. Distribution switches
d. Access layer switches
10. In a properly designed hierarchical network, a broadcast from one PC is confined to which one of the following?
a. One access layer switch port
b. One access layer switch
c. One switch block
d. The entire campus network
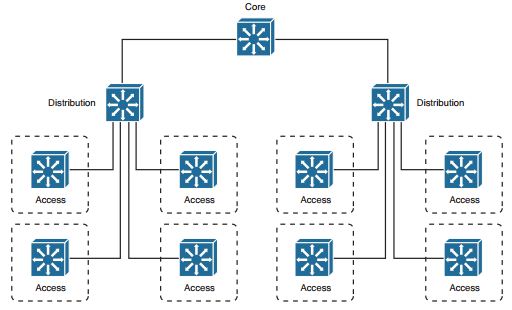
11. Which one or more of the following are the components of a typical switch block?
a. Access layer switches
b. Distribution layer switches
c. Core layer switches
d. E-commerce servers
e. Service provider switches
12. Which of the following are common types of core, or backbone, designs? (Choose all that apply.)
a. Collapsed core
b. Loop-free core
c. Dual core
d. Layered core
e. Multinode core
13. What is the maximum number of access layer switches that can connect into a single distribution layer switch?
a. 1
b. 2
c. Limited only by the number of ports on the access layer switch
d. Limited only by the number of ports on the distribution layer switch
e. Unlimited
14. A switch block should be sized according to which two of the following parameters? (Choose all that apply.)
a. The number of access layer users
b. A maximum of 250 access layer users
c. A study of the traffic patterns and flows
d. The amount of rack space available
e. The number of servers accessed by users
15. What evidence can be seen when a switch block is too large? (Choose all that apply.)
a. IP address space is exhausted.
b. You run out of access layer switch ports.
c. Broadcast traffic becomes excessive.
d. Traffic is throttled at the distribution layer switches.
e. Network congestion occurs.
16. How many distribution switches should be built into each switch block?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 4
d. 8
17. Which are the most important aspects to consider when designing the core layer in a large network? (Choose all that apply.)
a. Low cost
b. Switches that can efficiently forward traffic, even when every uplink is at 100 percent capacity
c. High port density of high-speed ports
d. A low number of Layer 3 routing peer
More Resources