CCNP Security FAQ: Authorization Policies
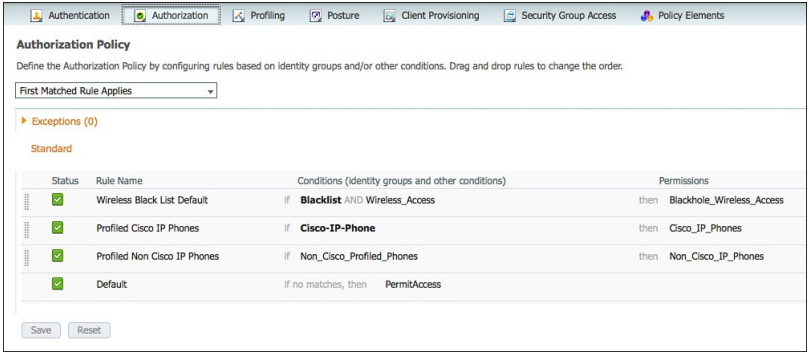
Figure: Default authorization policy
Q1. What is an authorization profile?
a. An authorization profile is a rule in the policy table that is formatted like “IF condition THEN result.”
b. An authorization profile is created to determine which identity store to validate the credentials with.
c. An authorization profile is a sequential list of identity stores to validate the credentials with.
d. An authorization profile is the mandatory result of an authorization rule.
Q2. What is the purpose of an authorization profile?
a. It contains the TACACS+ response (Access-Accept or Access-Reject) along with the additional authorization attributes to be sent to the network device for enforcement.
b. It contains the RADIUS response (Access-Accept or Access-Reject) along with the additional authorization attributes to be sent to the network device for enforcement.
c. It contains the RADIUS response (Continue or Terminate) along with additional authorization attributes to be sent to the network device for enforcement.
d. It contains the TACACS+ response (Continue or Terminate) along with additional authorization attributes to be sent to the network device for enforcement.
Q3. Which of the following options are part of the common tasks section of an authorization profile?
a. Access-Type (Continue or Terminate), DACL-Name, Web-Redirection, Auto Smart Port
b. Access-Type (Accept or Reject), DACL-Name, Web-Redirection, Auto Smart Port
c. DACL-Name, Role-Assignment, Local WebAuth, Auto Smart Port
d. DACL-Name, Web-Redirection, Local WebAuth, Auto Smart Port
Q4. Which of the following is correct?
a. An authorization policy contains authorization rules. Each rule will have at least one authorization profile.
b. An authorization rule contains authorization policies. Each policy will have at least one authorization profile.
c. An authentication policy contains authorization rules. Each rule must have an authentication result.
d. An authentication rule contains the authorization profiles. Each profile must contain one authentication result.
Q5. True or False? Condition attributes can be saved into a library for future use and improved readability.
a. True
b. False
Q6. What is special about the authorization profile required for an IP phone?
a. It contains the DNS name or IP address of the Cisco Call Manager Server.
b. It contains the voice domain permission AV pair, which authorizes the endpoint to access the voice VLAN assigned to the interface.
c. It contains the value for DHCP option 43, which provides the IP address of the Cisco Call Manager Server.
d. It contains the voice domain permission macro, which reconfigures the switch port to be a voice interface.
Q7. What is the difference between a simple condition and compound condition?
a. Simple conditions are easier to use than compound conditions.
b. Simple conditions are created on-the-fly within the expression builder, while compound conditions must be created separately.
c. Simple conditions contain only one attribute. Compound conditions contain multiple attributes along with an operator such as AND or OR.
d. Simple conditions and compound conditions can each contain multiple attributes, but compound conditions can mix operators such as AND or OR.
Q8. True or False? A compound condition can contain a mixture of simple conditions and raw attributes.
a. True
b. False
Q9. What should be the end goal of a Secure Access deployment?
a. To provide full access to the network, so security devices such as an ASA firewall can provide defense-in-depth
b. To provide full access to the network, as long as the authentication is successful, and provide limited access to any failed authentications
c. To secure the network by purchasing Cisco ISE, thereby increasing the stock value of the company
d. To provide very specific permissions to any authorization, providing defense-in-depth
Q10. What is unique about Cisco’s downloadable Access Control Lists (dACLs)?
a. Cisco dACLs allow the RADIUS server to apply ACLs that exist on the switch simply by sending the name of the ACL in the RADIUS AV pairs, while non-Cisco network devices cannot apply ACLs.
b. Cisco downloadable ACLs are created by experts at Cisco and published to Cisco.com where Cisco ISE can download the ACLs.
c. Cisco dACLs are created entirely on the RADIUS server, and the full ACL is sent down to the network device within RADIUS AV pairs, while non-Cisco network devices must create the ACL on the individual local network device.
d. Cisco dACLs are unique because they are downloaded from ISE and applied to the Cisco ASA that is in the network path, relieving the network device from the burden of traffic control.