CCNP Route FAQ: Policy-Based Routing and IP Service Level Agreement
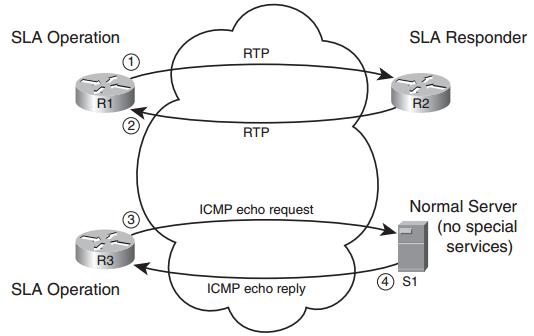
Figure: Sending and Receiving Packets with IP SLA
Q1. Policy-Based Routing (PBR) has been enabled on Router R1’s interface F0/0. Which of the following is true regarding how PBR works? (Choose two.)
a. Packets entering F0/0 will be compared based on the PBR route map.
b. Packets exiting F0/0 will be compared based on the PBR route map.
c. IOS ignores the PBR forwarding directions when the packet matches a route map deny clause.
d. IOS ignores the PBR forwarding directions when the packet matches a route map permit clause.
Q2. Examine the following configuration on Router R1. R1’s show ip route 172.16.4.1 command lists a route with outgoing interface S0/1/1. Host 172.16.3.3 uses telnet to connect to host 172.16.4.1. What will Router R1 do with the packets generated by host 172.16.3.3 because of the telnet, assuming the packets enter R1’s F0/0 interface? (Choose two.)
interface Fastethernet 0/0 ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip policy route-map Q2 ! route-map Q2 permit match ip address 101 set interface s0/0/1 ! access-list 101 permit tcp host 172.16.3.3 172.16.4.0 0.0.0.255
a. The packet will be forwarded out S0/0/1, or not at all.
b. The packet will be forwarded out S0/0/1 if it is up.
c. The packet will be forwarded out S0/1/1 if it is up.
d. The packet will be forwarded out S0/1/1 if it is up, or if it is not up, out s0/0/1.
e. The packet will be forwarded out S0/0/1 if it is up, or if it is not up, out s0/1/1.
Q3. The following output occurs on Router R2. Which of the following statements can be confirmed as true based on the output from R2?
R2# show ip policy Interface Route map Fa0/0 RM1 Fa0/1 RM2 S0/0/0 RM3
a. R2 will forward all packets that enter Fa0/0 per the PBR configuration.
b. R2 will use route map RM2 when determining how to forward packets that exit interface Fa0/1.
c. R2 will consider using PBR for all packets exiting S0/0/0 per route map RM3.
d. R2 will consider using PBR for all packets entering S0/0/0 per route map RM3.
Q4. Which of the following are examples of traffic that can be created as part of an IP Service-Level Agreement operation? (Choose two.)
a. ICMP Echo
b. VoIP (RTP)
c. IPX
d. SNMP
Q5. The following configuration commands exist only in an implementation plan document. An engineer does a copy/paste of these commands into configuration mode on Router R1. Which of the following answers is most accurate regarding the results?
ip sla 1 icmp-echo 1.1.1.1 source-ip 2.2.2.2 ip sla schedule 1 start-time now life forever
a. The SLA operation will be configured but will not start until additional commands are used.
b. The SLA operation is not completely configured so it will not collect any data.
c. The SLA operation is complete and working, collecting data into the RTTMON MIB.
d. The SLA operation is complete and working but will not store the data in the RTTMON MIB without more configuration.
Answer: C. The three lines shown create the operation number (first command), define the operation (second command), and start the operation (third command). All commands are correct. After the operation is started, IP SLA stores the data in the RTTMON MIB–no additional configuration necessary.
Q6. The following output occurs on Router R1. IP SLA operation 1 uses an ICMP echo operation type, with default frequency of 60 seconds. The operation pings from address 1.1.1.1 to address 2.2.2.2. Which of the following answers is true regarding IP SLA and object tracking on R1?
R1# show track Track 2 IP SLA 1 state State is Up 3 changes, last change 00:00:03 Delay up 45 secs, down 55 secs Latest operation return code: OK Latest RTT (millisecs) 6 Tracked by: STATIC-IP-ROUTING 0
a. The tracking return code fails after the SLA operation results in an ICMP echo failure three times.
b. The tracking return code fails after the SLA operation results in an ICMP echo failure one time.
c. After the tracking object fails, the tracking object moves back to an up state 45 seconds later in all cases.
d. After moving to a down state, the tracking object moves back to an OK state 45 seconds after the SLA operation moves to an OK state.