CCNP Route FAQ: Managing Scalable Network Growth
Q1. State two reasons to use an IP tunnel.
Answer: The following are reasons to use an IP tunnel:
- To solve problems with discontiguous networks
- To simplify network administration
- To tunnel desktop protocols through an IP-only backbone
Q2. State instances when access lists may be used for something other than filtering traffic.
Answer: Access lists may be used for the following:
- Queuing
- Policy routing
- QoS
- Filtering routing updates
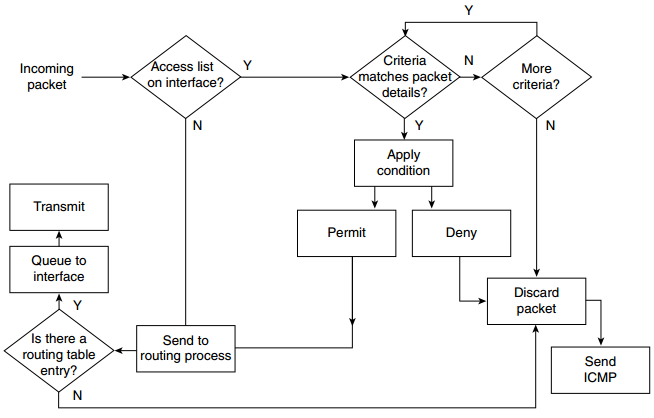
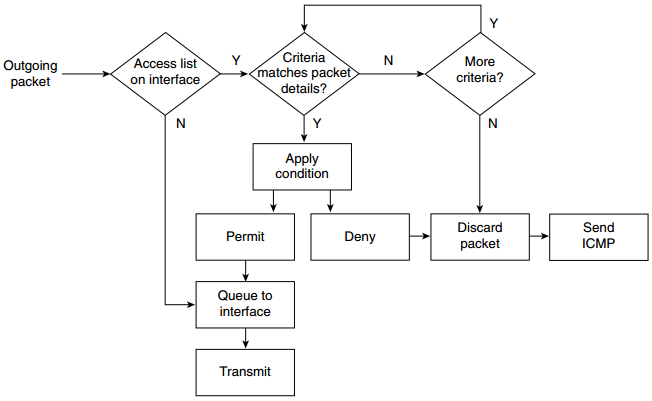
Figure: Processing of an IP Access List—Incoming and Outgoing Packets
Q3. In configuring an IP tunnel, how many IP tunnels may be created with the same source and destination address?
Q4. Associate the appropriate IOS feature to solve the network congestion problem experienced on the network in the following table.
| Network Congestion | Problem IOS Solution |
| Clients cannot connect to the centralized servers | Routing access list |
| Cisco environment in a large network with a large number of WAN connections | Prioritization on the interface |
| Large routing tables using RIP for IP | Reduction of the size of the broadcast domain by adding a router |
| Spanning tree is failing | IP helper address |
| SNA sessions are failing | EIGRP |
Answer: By matching the numbers in the following list you will have the correct answers:
| Network Congestion | Problem IOS Solution |
| Clients cannot connect to the centralized servers | 3. Routing access list |
| Cisco environment in a large network with a large number of WAN connections | 5. Prioritization on the interface |
| Large routing tables using RIP for IP | 4. Reduction of the size of the broadcast domain by adding a router |
| Spanning tree is failing | 1. IP helper address |
| SNA sessions are failing | 2. EIGRP |
Q5. Which command would prevent the router from forwarding data to a remote network without generating an ICMP message?
Q6. Identify two commands that might be used to verify the configuration of an IP access list configuration.
Answer: Two commands that might be used to verify the configuration of an IP access list configuration could be taken from the following list:
- show ip interface
- show access-list
- show running config
- show startup config
Q7. What UDP ports will the IP helper address forward automatically?
Q8. If the number of workstations increases on a physical segment, the user may experience delays. Give two reasons why this might occur.
Answer: As the number of workstations increases on a physical segment, the user may experience delays because of the following reasons:
- There are collisions that require retransmission.
- There is packet loss because buffers on devices are overflowing and require retransmission.
- The end systems could be slowing down because of excessive broadcast traffic.
Q9. State three considerations when deciding where to place extended IP access lists.
Answer: You should consider at least three of the following:
- Minimize the distance that denied traffic must travel. Place the access list as close to the source as possible.
- Keep the denied traffic off the backbone connecting buildings or campuses.
- Ensure that the router chosen can deal easily with the additional CPU requirements.
- Consider the CPU utilization because an inbound access list does not have to do a routing update on denied traffic.
- However, the interface may have to match the access list against more traffic.
- Consider the number of interfaces affected.
- Consider the number of nodes affected. Outbound access lists may afford greater granularity.
Consider access list management. - Consider the network growth and the effect on the management of the interfaces and the changing needs in connectivity.
Q10 What is the function of the access layer?
Q11. What is the access list number range for IP extended access lists?
Q12. What is priority queuing?
Q13. List two symptoms of network congestion.
Answer: Symptoms of network congestion include these:
- Applications timing out at end stations
- Clients not being capable of connecting to network resources
- Network death resulting
The causes of congestion are often the symptoms seen, and they include these:
- Excessive traffic, seen on the network-management tools
- Dropped packets, seen on the router interfaces
- The retransmission of packets, seen on the network-management tools
- Incomplete routing tables, seen on the router
- Incomplete service tables, seen on servers and routers
- Broadcast storms caused by spanning tree
Q14. If a switch has redundant links to another switch, what action would be taken if the Spanning-Tree Protocol fails to see a BPDU in time (within the MaxAge Timer value)?
Q15. How could the dropping of packets cause an increase of traffic on the network?
Q16. How might network congestion cause a loss of services?
Answer: Services may be lost when network congestion is experienced. The reasons include these:
- The input buffers of the server are overloaded.
- The application times out.
- The network traffic informing clients of services is lost or delayed sufficiently for the services to be dropped from the
- server lists.
Q17. In Cisco’s hierarchical design, what is the function of the core layer?
Q18. In Cisco’s hierarchical design, where is the access layer located?
Q19. In the hierarchical design suggested by Cisco, at which layer are access lists not recommended?
Q20. What is the function of the distribution layer?
Q21. If an access list is configured as an inbound list, will the packet be sent to the routing process?
Q22. State three uses of access lists.
Answer: The following are all valid uses for access lists:
- Restricting networks sent out in routing updates
- Restricting connectivity to remote networks
- Restricting the services advertised in an IPX network
- Restricting large packet sizes from traversing the network
Q23. In an IP standard access list, what is the default wildcard mask?
Q24. If a packet does not match any of the criteria in an access list, what action will be taken?
Q25. Why does the null interface not report an ICMP message stating that the packet is undeliverable?
Q26. How would you restrict Telnet connectivity to the router that you were configuring?
Q27. Which of the queuing techniques offered by the Cisco IOS are manually configured?
Q28. Explain ip helper address. What is its function?