CCNP Route FAQ: IP Addressing
Q1. Identify one criterion to help determine a subnet mask for classful addressing when designing a network-addressing scheme.
Answer: Questions to ask include the following:
- How many networks are there in the network?
- How many hosts are there on the largest subnet?
Q2. Which command is used to forward broadcast traffic across a router to a particular destination?
Q3. With a classless address of 204.1.64.0/20, what is the range of classful addresses that are included in the address? Write your answer in dotted decimal and the third octet in binary notation.
Answer: The address 204.1.64.0 /20 includes the Class C addresses 204.1.64.0 to 204.1.79.0; this is illustrated in both dotted decimal and binary notation in the following table.
| Binary Notation | Decimal Notation |
| 01000000 01000001 01000010 01000011 01000100 01000101 01000110 01000111 01001000 01001001 01001010 01001011 01001100 01001101 01001110 01001111 |
204.1.64.0 204.1.65.0 204.1.66.0 204.1.67.0 204.1.68.0 204.1.69.0 204.1.70.0 204.1.71.0 204.1.72.0 204.1.73.0 204.1.74.0 204.1.75.0 204.1.76.0 204.1.77.0 204.1.78.0 204.1.79.0 |
Q4. What is a discontiguous network?
Q5. For VLSM to be available as a design option in the network, what characteristic must the routing protocol possess?
Q6. If summarization is to be implemented in the network, name one design criterion for the addressing scheme that must be in place?
Q7. What networks are provided in RFC 1918, and what prefix mask accompanies each network?
Answer: The private addresses provided in RFC 1918 are as follows:
- 10.0.0.0 /8 to 255.0.0.0
- 172.16.0.0 /12 to 255.240.0.0
- 192.168.0.0 /16 to 255.255.0.0
Q8. If the host portion of a subnet has been used to identify end devices, can that subnet be used again for VLSM?
Q9. Describe the purpose of the ip forward-protocol command.
Q10. Which command is used on point-to-point lines to conserve IP address space?
Q11. Give one example of when route summarization would not be a good solution.
Answer: Route summarization is not useful in the following circumstances:
- There are discontiguous networks in the organization.
- A specific subnet needs to be seen throughout the network.
- The addressing scheme does not support summarization. No common highorder bits are shared in the network-addressing scheme.
- Access lists require detailed information.
Q12. Give one reason for implementing router summarization.
Answer: Route summarization is useful for the following reasons:
- To keep the routing tables small
- To keep the network overhead low
- To hide the network details from the rest of the organization
- To prevent flapping links from affecting the rest of the network
Q13. Given an address of 133.44.0.0 and a prefix mask of /25, how many networks can be addressed, and how many hosts can exist on each network? Write the first and last possible subnets in binary and decimal notation.
Binary Notation Decimal Notation
00000000.10000000 133.44.0.128
11111111.00000000 133.44.255.0
Q14. What class of address is 131.188.0.0, and how many hosts can be addressed if no subnetting is used?
Q15. If given a Class C address with the requirement to accommodate 14 subnets and 10 hosts on each subnet, what subnet mask would you use?
Q16. List the range of hosts available on the 136.122.10.192/28 subnet.
Q17. Convert the subnet address 56.98.5.0/24 to binary notation, and state the class to which it belongs.
00111000.01100010.00000101.00000000
Q18. Write out the decimal notation of the following subnet mask presented in the binary notation of 11111111.11111111.11111111.11111000.
Q19. What does VLSM stand for?
Q20. The Class B network address of 133.222.0.0 has been given a mask of 255.255.255.0. The subnets 133.222.8.0, 133.222.9.0, 133.222.10.0, 133.222.11.0, 133.222.12.0, Answer: 133.222.13.0, and 133.222.14.0 need to be summarized using VLSM. Give the subnet and new mask to achieve this summarization.
Q21. Is 201.111.16.0/20 a valid subnet mask?
Q22. Which routing protocols support VLSM?
Q23. Briefly define route summarization.
Q24. What sort of design scheme does route summarization require?
Q25. In route summarization, where is the subnet mask moved?
Q26. How does summarization allow for smaller routing tables?
Q27. Identify two private addresses defined in RFC 1918.
Answer: The RFC 1918 addresses that you can use are as follows:
- Class A: 10.0.0.0
- Class B range: 172.16.0.0 through 172.31.0.0
- Class C range: 192.168.1.0 through 192.168.254.0
Q28. What is a discontiguous network?
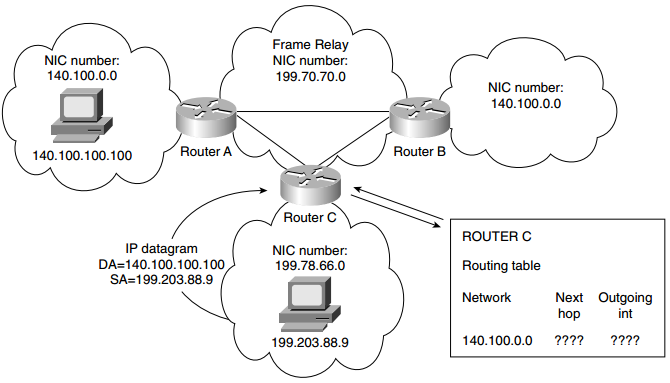
Figure: Discontiguous Networks
Q29. What does CIDR stand for?
Q30. Which RFC is responsible for first describing the use of subnet masking?