CCNA FAQ: OSPF
Q1. Which of the following affects the calculation of OSPF routes when all possible default values are used?
a. Bandwidth
b. Delay
c. Load
d. Reliability
e. MTU
f. Hop count
Q2. OSPF runs an algorithm to calculate the currently best route. Which of the following terms refer to that algorithm? (Choose two answers.)
a. SPF
b. DUAL
c. Feasible successor
d. Dijkstra
e. Good old common sense
Q3. Two OSPF routers connect to the same VLAN using their Fa0/0 interfaces. Which of the following settings on the interfaces of these two potentially neighboring routers would prevent the two routers from becoming OSPF neighbors? (Choose two answers.)
a. IP addresses of 10.1.1.1/24 and 10.1.1.254/25, respectively
b. The addition of a secondary IP address on one router’s interface, but not the other
c. Both router interfaces assigned to area 3
d. One router is configured to use MD5 authentication, and the other is not configured to use authentication
Q4. Which of the following OSPF neighbor states is expected when the exchange of topology information is complete so that neighboring routers have the same LSDB?
a. Two-way
b. Full
c. Exchange
d. Loading
Q5. Which of the following is true about an existing OSPF designated router? (Choose two answers.)
a. A newly connected router in the same subnet, with a higher OSPF priority, preempts the existing DR to become the new DR.
b. A newly connected router in the same subnet, with a lower OSPF priority, preempts the existing DR to become the new DR.
c. The DR may be elected based on the lowest OSPF Router ID.
d. The DR may be elected based on the highest OSPF Router ID.
e. The DR attempts to become fully adjacent with every other neighbor on the subnet.
Q6. Which of the following network commands, following the command router ospf 1, tells this router to start using OSPF on interfaces whose IP addresses are 10.1.1.1, 10.1.100.1, and 10.1.120.1?
a. network 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 area 0
b. network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
c. network 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.255 area 0
d. network 10.0.0.1 0.255.255.0 area 0
Q7. Which of the following network commands, following the command router ospf 1, tells this router to start using OSPF on interfaces whose IP addresses are 10.1.1.1, 10.1.100.1, and 10.1.120.1?
a. network 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 area 0
b. network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.0 area 0
c. network 10.1.1.0 0.x.1x.0 area 0
d. network 10.1.1.0 255.0.0.0 area 0
e. network 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 area 0
Q8. Which of the following commands list the OSPF neighbors off interface serial 0/0? (Choose three answers.)
a. show ip ospf neighbor
b. show ip ospf interface
c. show ip neighbor
d. show ip interface
e. show ip ospf neighbor serial 0/0
Q9. Routers R1, R2, and R3 connect to the same VLAN using their F0/0 interfaces. All three use OSPF, and all three have a neighbor relationship that reached a FULL state. R1’s configuration shows the ip ospf authentication command under interface F0/0. Which of the following statements is true regarding OSPF in this small part of the internetwork? (Choose two answers.)
a. R1 also has an ip ospf authentication-key command configured on that same interface.
b. R2’s show ip ospf neighbor command shows the use of simple password authentication.
c. R3’s show ip ospf interface f0/0 command shows the use of MD5 authentication.
d. R3 must also have an ip ospf authentication command configured on its F0/0 interface.
Q10. An OSPF router learns about six possible routes to reach subnet 10.1.1.0/24. All six routes have a cost of 55, and all six are interarea routes. By default, how many of these routes are placed in the routing table?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
e. 5
f. 6
Q11. What is the OSPF router ID, and how is it determined?
Q12. What is the significance of a designated router, and what circumstances are necessary for a router to become a DR?
Q13. What is the purpose of an OSPF area?
Q14. How does the DUAL algorithm use the contents of the topology table to ensure rapid convergence?
Q15. What are the basic configuration steps for using OSPF and EIGRP routing protocols?
Q16. David, your Cisco coworker, shows you the following output from a debug ip ospf events command:

He knows that the Rs stand for received and the Cs stand for configured. However, he can’t figure out why he cannot get OSPF to work. What should you tell him?
A. OSPF needs to have the classful networks advertised.
B. Area 51 is an invalid area number.
C. Check the OSPF timers.
D. 10.1.42.100 needs to be a DR.
Q17. Given the following output, which of the following statements is false?

A. This router will listen for updates on multicast address 224.0.0.6.
B. 10.1.1.1 is not a loopback IP address.
C. The router interface is not connected to the backbone area.
D. This router will listen for LSA hellos on 224.0.0.5.
Q18. Given the following customer requirements, which routing protocol would you recommend?
Requirements: fast convergence, IP only, large network, VLSM support needed, Cisco and Nortel routers.
A. RIPv2
B. RIPv1
C. EIGRP
D. OSPF
Q19. Based on the following output, which of the following statements are true? (Choose two)

A. The route for 172.17.0.0 is down and is being queried.
B. Router 192.168.1.31 has a composite metric of 2297856 to get to 172.17.0.0.
C. Router 192.168.1.6 has an administrative distance of 2195456.
D. There is no feasible successor to 172.17.0.0.
20. Given the following output, why is OSPF not working correctly?

A. The network ID and wildcard mask are incorrect.
B. The area needs to be configured as a stub area.
C. You need the no auto-summary command to make OSPF classless.
D. The autonomous system number doesn’t match other router configurations.
Q21. Given the following output, what will the OSPF router ID be for this router if you configure it for OSPF?

A. OSPF does not require a router ID because this router has a broadcast topology.
B. 172.16.0.1
C. 10.1.42.1
D. 192.168.1.5
Q22. What is the cost of a 512kbps link for OSPF?
A. 156
B. 195
C. 10
D. 64
Q23. What is the effect of the following configuration?

A. Only interface Fast Ethernet 0/0’s subnet will be associated into OSPF area 10.
B. Only interface Serial 0/0/0’s subnet will be associated into OSPF area 10.
C. Only interface Serial 0/0/1’s subnet will be associated into OSPF area 10.
D. None of the above
Q24. Which command enables unequal load balancing over all three links with the metrics Network A-234, Network B-23, and Network C-601?
A. variance 10
B. variance 3
C. variance 30
D. variance 25
Q25. What would be the result of the following two configurations?

A. Router A adds the 172.18.0.0 network to its routing table.
B. Router B does not add the 192.168.34.0 network, because it is advertising it to Router A.
C. The routing updates do not contain the subnet masks.
D. Router A and Router B ignore each other’s updates.
Q26. Which of the following characteristics does not apply to EIGRP and OSPF?
A. The timers for hello/dead differ depending on the topology.
B. Both routing protocols support VLSM, router summarization, and discontiguous networks by default.
C. Both routing protocols have a routing table, neighbor table, and topology table.
D. Both routing protocols discover neighbors by sending hellos to a multicast address.
Q27. There are three possible routes for a router to reach a destination network. The first route is from OSPF with a metric of 782. The second route is from RIPv2 with a metric of 4. The third is from EIGRP with a composite metric of 20514560. Which route will be installed by the router in its routing table?
A. RIPv2
B. EIGRP
C. OSPF
D. All three
Q28. In the accompanying diagram, which of the routers must be ABRs? (Choose all that apply.)

Answer: A, B, C. Any router that is member of two areas must be an area border router or ABR.
Q29. Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two.)
A. It is locally significant.
B. It is globally significant.
C. It is needed to identify a unique instance of an OSPF database.
D. It is an optional parameter required only if multiple OSPF processes are running on the router.
E. All routes in the same OSPF area must have the same process ID if they are to exchange routing information.
Q30. All of the following must match for two OSPF routers to become neighbors except which?
A. Area ID
B. Router ID
C. Stub area flag
D. Authentication password if using one
Q31. In the diagram, by default what will be the router ID of Lab_B?

A. 10.255.255.82
B. 10.255.255.9
C. 192.168.10.49
D. 10.255.255.81
Q32. You get a call from a network administrator who tells you that he typed the following into his router:
Router(config)#router ospf 1
Router(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 area 0
He tells you he still can’t see any routes in the routing table. What configuration error did the administrator make?
A. The wildcard mask is incorrect.
B. The OSPF area is wrong.
C. The OSPF process ID is incorrect.
D. The AS configuration is wrong.
Q33. Which of the following statements is true with regard to the output shown?
Corp#sh ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 172.31.1.4 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:34 10.10.10.2 FastEthernet0/0 192.168.20.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:31 172.16.10.6 Serial0/1 192.168.10.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:32 172.16.10.2 Serial0/0
A. There is no DR on the link to 192.168.20.1.
B. The Corp router is the BDR on the link to 172.31.1.4.
C. The Corp router is the DR on the link to 192.168.20.1.
D. The link to 192.168.10.1 is Active.
Q34. What is the administrative distance of OSPF?
A. 90
B. 100
C. 120
D. 110
Q35. In OSPF, Hellos are sent to what IP address?
A. 224.0.0.5
B. 224.0.0.9
C. 224.0.0.10
D. 224.0.0.1
Q36. What command generated the following output?
172.31.1.4 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:34 10.10.10.2 FastEthernet0/0 192.168.20. 1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:31 172.16.10.6 Serial0/1 192.168.10. 1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:32 172.16.10.2 Serial0/0
A. show ip ospf neighbor
B. show ip ospf database
C. show ip route
D. show ip ospf interface
Q37. Updates addressed to 224.0.0.6 are destined for which type of OSPF router?
A. DR
B. ASBR
C. ABR
D. All OSPF routers
Q38. For some reason, you cannot establish an adjacency relationship on a common Ethernet link between two routers. Looking at this output, what is the cause of the problem?
RouterA# Ethernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address 172.16.1.2/16, Area 0 Process ID 2, Router ID 172.126.1.2, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 10 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1 Designated Router (ID) 172.16.1.2, interface address 172.16.1.1 No backup designated router on this network Timer intervals configured, Hello 5, Dead 20, Wait 20, Retransmit 5 RouterB# Ethernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address 172.16.1.1/16, Area 0 Process ID 2, Router ID 172.126.1.1, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 10 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1 Designated Router (ID) 172.16.1.1, interface address 172.16.1.2 No backup designated router on this network Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
A. The OSPF area is not configured properly.
B. The priority on RouterA should be set higher.
C. The cost on RouterA should be set higher.
D. The Hello and Dead timers are not configured properly.
E. A backup designated router needs to be added to the network.
F. The OSPF process ID numbers must match.
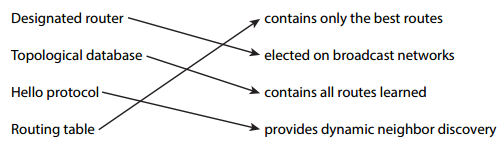
Q39. In the work area match each OSPF term (by line) to its definition.
Designated router contains only the best routes
Topological database elected on broadcast networks
Hello protocol contains all routes learned
Routing table provides dynamic neighbor discovery
Q40. Type the command that will disable OSPF on the Fa0/1 interface under the routing process. Write only the command and not the prompt.
Q41. Which two of the following commands will place network 10.2.3.0/24 into area 0? (Choose two.)
A. router eigrp 10
B. router ospf 10
C. router rip
D. network 10.0.0.0
E. network 10.2.3.0 255.255.255.0 area 0
F. network 10.2.3.0 0.0.0.255 area0
G. network 10.2.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Q42. Given the following output, which statement or statements can be determined to be true? (Choose all that apply.)
RouterA2# show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 192.168.23.2 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:29 10.24.4.2 FastEthernet1/0 192.168.45.2 2 FULL/BDR 00:00:24 10.1.0.5 FastEthernet0/0 192.168.85.1 1 FULL/- 00:00:33 10.6.4.10 Serial0/1 192.168.90.3 1 FULL/DR 00:00:32 10.5.5.2 FastEthernet0/1 192.168.67.3 1 FULL/DR 00:00:20 10.4.9.20 FastEthernet0/2 192.168.90.1 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:23 10.5.5.4 FastEthernet0/1 <<output omitted>>
Q43. What are three reasons for creating OSPF in a hierarchical design? (Choose three.)
A. To decrease routing overhead
B. To speed up convergence
C. To confine network instability to single areas of the network
D. To make configuring OSPF easier
Q44. Type the command that produced the following output. Write only the command and not the prompt.
FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address 10.10.10.1/24, Area 0 Process ID 1, Router ID 223.255.255.254, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1 Designated Router (ID) 223.255.255.254, Interface address 10.10.10.1 Backup Designated router (ID) 172.31.1.4, Interface address 10.10.10.2 Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 oob-resync timeout 40 Hello due in 00:00:08 Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS) Cisco NSF helper support enabled IETF NSF helper support enabled Index 3/3, flood queue length 0 Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1 Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1 Adjacent with neighbor 172.31.1. Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
Q45. A(n) ____________is an OSPF data packet containing link-state and routing information that are shared among OSPF routers.
A. LSA
B. TSA
C. Hello
D. SPF
Q46. If routers in a single area are configured with the same priority value, what value does a router use for the OSPF router ID in the absence of a loopback interface?
A. The lowest IP address of any physical interface
B. The highest IP address of any physical interface
C. The lowest IP address of any logical interface
D. The highest IP address of any logical interface
Q47. Which of the following are scalability issues with single-area OSPF networks? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Size of the routing table
B. Size of the OSPF database
C. Maximum hop-count limitation
D. Recalculation of the OSPF database
Q48. Which of the following describes a router that connects to an external routing process (e.g., EIGRP)?
A. ABR
B. ASBR
C. Type 2 LSA
D. Stub router
Q49. Which of the following must match in order for an adjacency to occur between routers? (Choose three.)
A. Process ID
B. Hello and dead timers
C. Link cost
D. Area
E. IP address/subnet mask
Q50. Which OSPF state do two routers forming an adjacency appear as in the show ip ospf neighbor output after adding neighbors into the table and exchanging hello information?
A. ATTEMPT
B. INIT
C. 2WAY
D. EXSTART
E. FULL
Q51. You need to set up a preferred link that OSPF will use to route information to a remote network. Which command will allow you to set the interface link as preferred over another?
A. ip ospf preferred 10
B. ip ospf priority 10
C. ospf bandwidth 10
D. ip ospf cost 10
Q52. When would a router’s neighbor table show the FULL/DR state?
A. After the first Hello packets are received by a neighbor
B. When all information is synchronized among adjacent neighbors
C. When the router’s neighbor table is too full of information and is discarding neighbor information
D. After the EXSTART state
Q53. Which is/are true regarding OSPFv3? (Choose all that apply.)
A. You must add network statements under the OSPF process.
B. There are no network statements in OSPFv3 configurations.
C. OSPFv3 uses a 128-bit RID.
D. If you have IPv4 configured on the router, it is not mandatory that you configure the RID.
E. If you don’t have IPv4 configured on the router, it is mandatory that you configure the RID.
F. OSPFv3 doesn’t use LSAs like OSPFv2 does.
Q54. What is the default cost of a Fast Ethernet interface configured with OSPF?
A. 1
B. 10
C. 100
D. 1,000
Q55. Which type of LSA is generated by DRs and referred to as a network link advertisement (NLA)?
A. Type 1
B. Type 2
C. Type 3
D. Type 4
E. Type 5
Q56. Which type of LSA is generated by ABRs and refers to a summary link advertisement (SLA)?
A. Type 1
B. Type 2
C. Type 3
D. Type 4
E. Type 5
Q57. Which command will show all the LSAs known by a router?
A. show ip ospf
B. show ip ospf neighbor
C. show ip ospf interface
D. show ip ospf database
Q58. Using the following illustration, what is the cost from R1’s routing table to reach the network with Server 1? Each Gigabit Ethernet link has a cost of 4, and each serial link has a cost of 15.

A. 100
B. 23
C. 64
D. 19
E. 27
Q59. Using the following illustration, which of the following are true? (Choose all that apply.)

A. R1 is an internal router.
B. R3 would see the networks connected to the R1 router as an inter-area route.
C. R2 is an ASBR.
D. R3 and R4 would receive information from R2 about the backbone area, and the same LSA information would be in both LSDBs.
E. R4 is an ABR.
Q60. Which of the following could cause two routers to not form an adjacency? (Choose all that apply.)
A. They are configured in different areas.
B. Each router sees the directly connected link as different costs.
C. Two different Process ID’s configured.
D. ACL is configured on the routing protocol.
E. IP address/mask.
F. Passive interface is configured.
Q61. Which of the following IOS commands shows the state of an adjacency with directly connected routers?
A. debug ospf events
B. show ip ospf border-routers
C. show ip ospf neighbor
D. show ip ospf database
Q62. What command will show you the DR and DBR address of the area you are connected to directly with an interface?
A. show interface s0/0/0
B. show interface fa0/0
C. show ip ospf interface s0/0/0
D. show ip ospf interface fa0/0
Q63. Which of the following could be causing a problem with the Corp router not forming an adjacency with its neighbor router? (Choose all that apply.)

A. The routers are configured with the wrong network statements.
B. They have different maximum paths configured.
C. There is a passive interface configured.
D. There is an ACL set stopping Hellos.
E. The costs of the links between the routers are configured differently.
F. They are in different areas.
Q64. Which of the following is/are true? (Choose all that apply.)
A. The reference bandwidth for OSPF and OSPFv3 is 1.
B. The reference bandwidth for OSPF and OSPFv3 is 100.
C. You change the reference bandwidth from global config with the command auto-cost reference bandwidth number.
D. You change the reference bandwidth under the OSPF router process with the command auto-cost reference bandwidth number.
E. Only one router needs to set the reference bandwidth if it is changed from its default.
F. All routers in a single area must set the reference bandwidth if it is changed from its default.
G. All routers in the AS must set the reference bandwidth if it is changed from its default.
Q65. Which of the following interfaces would have the same default cost? (Choose two.)
A. Fast Ethernet
B. Ethernet
C. Serial
D. Gigabit Ethernet
Q66. What is the default cost of a serial interface with OSPF?
A. 1
B. 10
C. 32
D. 64
E. 100
[mks_button size=”medium” title=”CCNA Frequently Asked Questions” style=”squared” url=”https://www.configrouter.com/cisco-certified-network-associate-faq/” target=”_blank” bg_color=”#000000″ txt_color=”#FFFFFF” icon=”” icon_type=”” nofollow=”0″] [mks_button size=”medium” title=”CCNA Exam Questions with Explanation” style=”squared” url=”https://www.configrouter.com/ccna-online-training/” target=”_blank” bg_color=”#000000″ txt_color=”#FFFFFF” icon=”” icon_type=”” nofollow=”0″]