CCNA DC FAQ: Fundamentals of IPv4 Addressing and Routing
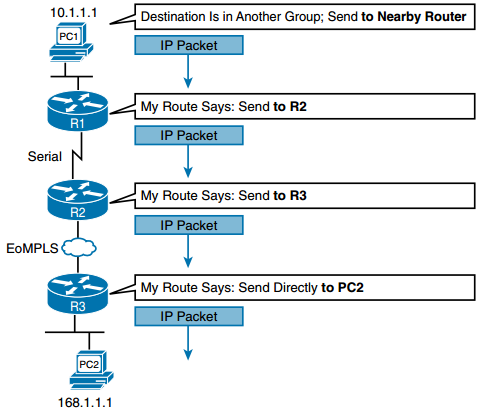 Figure: Routing Logic: PC1 Sending an IP Packet to PC2
Figure: Routing Logic: PC1 Sending an IP Packet to PC2
Q1. Which of the following are functions of OSI Layer 3 protocols? (Choose two answers.)
a. Logical addressing
b. Physical addressing
c. Path selection
d. Arbitration
e. Error recovery
Q2. Imagine that PC1 needs to send some data to PC2, and PC1 and PC2 are separated by several routers. Both PC1 and PC2 sit on different Ethernet LANs. What are the largest entities (in size) that make it from PC1 to PC2? (Choose two answers.)
a. Frame
b. Segment
c. Packet
d. L5 PDU
e. L3 PDU
f. L1 PDU
Q3. Which of the following is a valid Class C IP address that can be assigned to a host?
a. 1.1.1.1
b. 200.1.1.1
c. 128.128.128.128
d. 224.1.1.1
Q4. What is the assignable range of values for the first octet for Class A IP networks?
a. 0 to 127
b. 0 to 126
c. 1 to 127
d. 1 to 126
e. 128 to 191
f. 128 to 192
Q5. PC1 and PC2 are on two different Ethernet LANs that are separated by an IP router. PC1’s IP address is 10.1.1.1, and no subnetting is used. Which of the following addresses could be used for PC2? (Choose two answers.)
a. 10.1.1.2
b. 10.2.2.2
c. 10.200.200.1
d. 9.1.1.1
e. 225.1.1.1
f. 1.1.1.1
Q6. Imagine a network with two routers that are connected with a point-to-point HDLC serial link. Each router has an Ethernet, with PC1 sharing the Ethernet with Router1 and PC2 sharing the Ethernet with Router2. When PC1 sends data to PC2, which of the following is true?
a. Router1 strips the Ethernet header and trailer off the frame received from PC1, never to be used again.
b. Router1 encapsulates the Ethernet frame inside an HDLC header and sends the frame to Router2, which extracts the Ethernet frame for forwarding to PC2.
c. Router1 strips the Ethernet header and trailer off the frame received from PC1, which is exactly re-created by Router2 before forwarding data to PC2.
d. Router1 removes the Ethernet, IP, and TCP headers and rebuilds the appropriate headers before forwarding the packet to Router2.
Q7. Which of the following does a router normally use when making a decision about routing TCP/IP packets?
a. Destination MAC address
b. Source MAC address
c. Destination IP address
d. Source IP address
e. Destination MAC and IP address
Q8. Which of the following are true about a LAN-connected TCP/IP host and its IP routing (forwarding) choices? (Choose two answers.)
a. The host always sends packets to its default gateway.
b. The host sends packets to its default gateway if the destination IP address is in a different class of IP network than the host.
c. The host sends packets to its default gateway if the destination IP address is in a different subnet than the host.
d. The host sends packets to its default gateway if the destination IP address is in the same subnet as the host.
Q9. Which of the following are functions of a routing protocol? (Choose two answers.)
a. Advertising known routes to neighboring routers
b. Learning routes for subnets directly connected to the router
c. Learning routes, and putting those routes into the routing table, for routes advertised to the router by its neighboring routers
d. Forwarding IP packets based on a packet’s destination IP address
Q10. A company implements a TCP/IP network, with PC1 sitting on an Ethernet LAN. Which of the following protocols and features requires PC1 to learn information from some other server device?
a. ARP
b. ping
c. DNS
d. None of these answers is correct.