CCIE SP MPLS FAQ: Advanced MPLS/VPN Topologies
Q1. In the context of the MPLS VPN architecture, describe how to create an extranet.
Answer: Import the routes from a VRF into a different VRF that provides connectivity for another VPN.
Q2. When provisioning an extranet, can two organizations that use the same IP addressing structure communicate?
Answer: Yes. However, this requires the deployment of Network Address Translation (NAT) and would usually be provisioned using one or more common central sites.
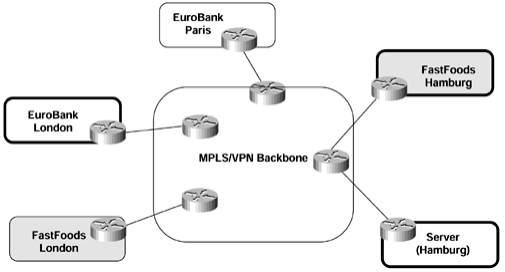
Q3. List some of the services that might be available through use of the central services topology.
Answer: Application hosting, access to shared equipment, such as voice gateways, and centralized network management.
Figure: Central Services in SuperCom Network
Q4. How are the spoke sites within a central services topology prevented from communicating directly with other spoke sites?
Answer: Through the use of different RT values than on the central site. Each spoke imports only routes that contain the RT value of the central site.
Q5. In the hub-and-spoke topology, how does the hub site attract spoke-tospoke traffic?
Answer: The hub site attracts spoke-to-spoke traffic by importing the spoke RT into the hub VRF and re-exporting the routes using a different RT, which is imported into the spoke VRFs.
Q6. For which type of topology is the AllowAS-in feature required and why?
Answer: The hub-and-spoke topology because the hub site receives updates that contain its own AS number and, therefore, drops the routes if AllowAS is not enabled.
More Resources