CCDA FAQ: Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4)
Q1. List the RFC 1918 private address ranges.
Q2. True or false: You can use DHCP to specify the TFTP host’s IP address to a client PC.
Q3. True or false: 255.255.255.248 and /28 are two representations of the same IP mask.
Q4. True or false: Upper-layer protocols are identified in the IP header’s protocol field. TCP is protocol 6, and UDP is protocol 17.
Q5. Fill in the blank: Without any options, the IP header is _________ bytes in length.
Q6. The IP header’s ToS field is redefined as the DS field. How many bits does DSCP use for packet classification, and how many levels of classification are possible?
Q7. True or false: NAT uses different IP addresses for translations. PAT uses different port numbers to identify translations.
Q8. True or false: The IP header’s header checksum field performs the checksum of the IP header and data.
Q9. Calculate the subnet, the address range within the subnet, and the subnet broadcast of the address 172.56.5.245/22.
Q10. When packets are fragmented at the network layer, where are the fragments reassembled?
Q11. Which protocol can you use to configure a default gateway setting on a host?
a. ARP
b. DHCP
c. DNS
d. RARP
Q12. How many host addresses are available with a Class B network with the default mask?
a. 63,998
b. 64,000
c. 65,534
d. 65,536
Q13. Which of the following is a dotted-decimal representation of a /26 prefix mask?
a. 255.255.255.128
b. 255.255.255.192
c. 255.255.255.224
d. 255.255.255.252
Q14. Which network and mask summarize both the 192.170.20.16/30 and 192.170.20.20/30 networks?
a. 192.170.20.0/24
b. 192.170.20.20/28
c. 192.170.20.16/29
d. 192.170.20.0/30
Q15. Which AF class is backward compatible with IP precedence bits’ flash traffic?
a. AF2
b. AF3
c. AF4
d. EF
Q16. Which of the following is true about fragmentation?
a. Routers between source and destination hosts can fragment IPv4 packets.
b. Only the first router in the network can fragment IPv4 packets.
c. IPv4 packets cannot be fragmented.
d. IPv4 packets are fragmented and reassembled at each link through the network.
Q17. A packet sent to a multicast address reaches what destinations?
a. The nearest destination in a set of hosts.
b. All destinations in a set of hosts.
c. Broadcasts to all hosts.
d. Reserved global destinations.
Q18. What are three types of IPv4 addresses?
a. Anycast
b. Multicast
c. Dynamic
d. Broadcast
e. Unicast
f. Global
g. Static
Q19. Which devices should be assigned an IP address dynamically? (Select three.)
a. Cisco IP phones
b. LAN switches
c. Workstations
d. Mobile devices
e. Routers
Q20. Which name resolution method reduces administrative overhead?
a. Static name resolution
b. Dynamic name resolution
c. DHCP name resolution
d. Host.txt name resolution
Q21. How many hosts can be addressed with the following IPv4 subnet: 172.30.192.240/28?
a. 6
b. 14
c. 126
d. 1024
Q22. What is the smallest subnet and mask that can be used in a DMZ network that needs to have only three hosts?
a. 192.168.10.32/30
b. 192.168.10.32/29
c. 192.168.10.32/28
d. 192.168.10.32/27
Answer the following questions based on the given Figure. Company VWX has the network shown in Figure 8-9. The main site has three LANs, with 100, 29, and 60 hosts. The remote site has two LANs, each with 100 hosts. The network uses private addresses. The Internet service provider assigned the company the network 210.200.200.8/26.
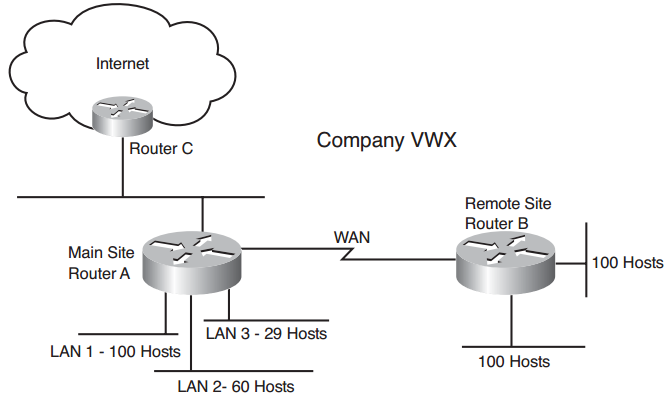
Q23. The remote site uses the network prefix 192.168.10.0/24. What subnets and masks can you use for the LANs at the remote site and conserve address space?
a. 192.168.10.64/26 and 192.168.10.192/26
b. 192.168.10.0/25 and 192.168.10.128/25
c. 192.168.10.32/28 and 192.168.10.64/28
d. 192.168.10.0/30 and 192.168.10.128/30
Q24. The main site uses the network prefix 192.168.15.0/24. What subnets and masks can you use to provide sufficient addresses for LANs at the main site and conserve address space?
a. 192.168.15.0/25 for LAN 1, 192.168.15.128/26 for LAN 2, and 172.15.192.0/27 for LAN 3
b. 192.168.15.0/27 for LAN 1, 192.168.15.128/26 for LAN 2, and 172.15.192.0/25 for LAN 3
c. 192.168.15.0/100 for LAN 1, 192.168.15.128/60 for LAN 2, and 172.15.192.0/29 for LAN 3
d. 192.168.15.0/26 for LAN 1, 192.168.15.128/26 for LAN 2, and 172.15.192.0/29 for LAN 3
Q25. Which network and mask would you use for the WAN link to save the most address space?
a. 192.168.11.240/27
b. 192.168.11.240/28
c. 192.168.11.240/29
d. 192.168.11.240/30
Q26. What networks does Router C announce to the Internet service provider’s Internet router?
a. 210.200.200.8/26
b. 192.168.10.0/24 and 192.168.11.0/24
c. 192.168.10.0/25 summary address
d. 201.200.200.8/29 and 192.168.10.0/25
Q27. What technology does Router C use to convert private addresses to public addresses?
a. DNS
b. NAT
c. ARP
d. VLSM
Q28. What mechanism supports the ability to divide a given subnet into smaller subnets based on need?
a. DNS
b. NAT
c. ARP
d. VLSM
Q29. Which of the following addresses is an IPv4 private address?
a. 198.176.1.1
b. 172.31.16.1
c. 191.168.1.1
d. 224.130.1.1
Q30. How many IP addresses are available for hosts in the subnet 198.10.100.64/27?
a. 14
b. 30
c. 62
d. 126
Q31. What subnet mask should you use in loopback addresses?
a. 255.255.255.252
b. 255.255.255.254
c. 255.255.255.0
d. 255.255.255.255
Q32. In what IPv4 field are the precedence bits located?
a. Priority field
b. IP Protocol field
c. Type of Service field
d. IP Options field
Q33. What type of address is 225.10.1.1?
a. Unicast
b. Multicast
c. Broadcast
d. Anycast
Q34. Which subnetworks are summarized by the following summary route: 150.10.192.0/21?
a. 150.10.192.0/24, 150.10.193.0/24
b. 150.10.192.0/22, 150.10.196.0/23, 150.10.197.0/24
c. 150.10.192.0/22, 150.10.199.0/22
d. 150.10.192.0/23, 150.10.194.0/23, 150.10.196.0/23, 150.10.197.0/24, 150.10.198.0/24
Q35. What type of network and subnet mask would you use to save address space in a point-to-point WAN link?
a. 100.100.10.16/26
b. 100.100.10.16/28
c. 100.100.10.16/29
d. 100.100.10.16/30
Q36. What is DHCP?
a. Dynamic Host Control Protocol
b. Dedicated Host Configuration Protocol
c. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
d. Predecessor to BOOTP
Q37. A company needs to use public IP addresses so that four network servers are accessible from the Internet. What technology is used to meet this requirement?
a. DNS
b. IPsec
c. Static NAT
d. Dynamic NAT
Q38. The DS field of DSCP is capable of how many codepoints?
a. 8
b. 32
c. 64
d. 128