CCDA FAQ: Enterprise LAN Design
Q1. What device filters broadcasts?
a. Layer 2 switch
b. Hub
c. Layer 3 switch
d. Router
e. A and C
f. C and D
g. A, C, and D
Q2. What is the maximum segment distance for Fast Ethernet over unshielded twistedpair (UTP)?
a. 100 feet
b. 500 feet
c. 100 meters
d. 285 feet
Q3. What device limits the collision domain?
a. Layer 2 switch
b. Hub
c. Layer 3 switch
d. Router
e. A and C
f. C and D
g. A, C, and D
Q4. The summarization of routes is a best practice at which layer?
a. Access layer
b. Distribution layer
c. Core layer
d. WAN layer
Q5. What type of LAN switches are preferred in the campus backbone of an enterprise network?
a. Layer 2 switches
b. Layer 3 switches
c. Layer 3 hubs
d. Hubs
Q6. Two workstations are located on separate VLANs. They exchange data directly. What type of application is this?
a. Client/server
b. Client-peer
c. Peer-peer
d. Client-enterprise
Q7. Which type of cable is the best solution in terms of cost for connecting an access switch to the distribution layer requiring 140 meters?
a. UTP
b. Copper
c. Multimode fiber
d. Single-mode fiber
Q8. Why is switching preferred over shared segments?
a. Shared segments provide a collision domain for each host.
b. Switched segments provide a collision domain for each host.
c. Shared segments provide a broadcast domain for each host.
d. Switched segments provide a broadcast domain for each host.
Q9. True or false: Layer 2 switches control network broadcasts.
Q10. What technology can you use to limit multicasts at Layer 2?
Q11. True or false: Packet marking is also called coloring.
Q12. True or false: Usually, the distribution and core layers are collapsed in medium-size networks.
Q13. What are two methods to mark frames to provide CoS?
Q14. Which of the following is an example of a peer-to-peer application?
a. IP phone call
b. Client accessing file server
c. Web access
d. Using a local server on the same segment
Q15. What primary design factors affect the design of a campus network? (Select three.)
a. Environmental characteristics
b. Number of file servers
c. Infrastructure devices
d. Fiber and UTP characteristics
e. Network applications
f. Windows, Linux, and mainframe operating systems
Q16. You need to connect a building access switch to the distribution switch. The cable distance is 135 m. What type of cable do you recommend?
a. UTP
b. Coaxial cable
c. Multimode fiber
d. Single-mode fiber
Q17. Which layer of the campus network corresponds to the data center aggregation layer?
a. Core layer
b. Distribution layer
c. Access layer
d. Server farm
Q18. Which of the following is an access layer best practice?
a. Reduce switch peering and routing
b. Use HSRP and summarize routes
c. Disable trunking and use RPVST+
d. Offload SSL sessions and use load balancers
Q19. Which of the following is a distribution layer best practice?
a. Reduce switch peering and routing
b. Use HSRP and summarize routes
c. Disable trunking and use RPVST+
d. Offload SSL sessions and use load balancers
Q20. Which of the following is a core layer best practice?
a. Reduce switch peering and routing
b. Use HSRP and summarize routes
c. Disable trunking and use RPVST+
d. Offload SSL sessions and use load balancers
Q21. Which of the following is a DC aggregation layer best practice?
a. Reduce switch peering and routing
b. Use HSRP and summarize routes
c. Disable trunking and use RPVST+
d. Offload SSL sessions and use load balancers
Q22. Which of the following are threats to the edge distribution?
a. IP spoofing
b. Network discovery
c. Packet-capture devices
d. All of the above
Q23. An enterprise network has grown to multiple buildings supporting multiple departments. Clients access servers that are in local and other buildings. The company security assessment has identified policies that need to be applied. What do you recommend?
a. Move all departments to a single building to prevent unauthorized access.
b. Move all servers to one of the LAN client segments.
c. Move all servers to a server farm segment that is separate from client LANs.
d. Move all servers to the building distribution switches.
Q24. Link redundancy and infrastructure services are design considerations for which layers?
a. Core layer
b. Distribution layer
c. Access layer
d. All of the above
Q25. Which of the following are server connectivity methods in the server farm?
a. Single NIC
b. EtherChannel
c. Content switch
d. All of the above
Q26. What is the recommended method to connect the distribution switches to the core?
a. Redundant triangle links
b. Redundant cross-connect links
c. Redundant Layer 3 squares
d. Redundant Layer 2 links
Q27. A campus network of four buildings is experiencing performance problems. Each building contains 400 to 600 devices, all in one IP subnet. The buildings are connected in a hub-and-spoke configuration back to building 1 using Gigabit Ethernet with multimode fiber. All servers are located in building 1. What do you recommend to improve performance?
a. Connect all buildings in a ring topology.
b. Implement multiple VLANs in each building.
c. Move servers to the buildings.
d. Use single-mode fiber to make the Gigabit Ethernet links faster.
Q28. What of the following is true about data link layer broadcasts?
a. Not controlled by routers
b. Not forwarded by routers
c. Not forwarded by switches
d. Not controlled by VLANs
Q29. Match each LAN medium with its original physical specification.
i. Fast Ethernet
ii. Gigabit Ethernet
iii. WLAN
iv. Token Ring
v. 10 Gigabit Ethernet
a. IEEE 802.3ab
b. IEEE 802.11b
c. IEEE 802.3u
d. IEEE 802.3ae
e. IEEE 802.5
Q30. True or false: Layer 3 switches bound Layer 2 collision and broadcast domains.
Q31. Match each LAN device type with its description.
i. Hub
ii. Bridge
iii. Switch
iv. Layer 3 switch
v. Router
a. Legacy device that connects two data link layer segments
b. Network layer device that forwards packets to serial interfaces connected to the WAN
c. High-speed device that forwards frames between two or more data link layer segments
d. High-speed device that bounds data link layer broadcast domains
e. Device that amplifies the signal between connected segments
Q32. Match each application type with its description.
i. Peer to peer
ii. Client-local server
iii. Client/server farm
iv. Client-enterprise edge
a. Server on the same segment
b. IM
c. Web access
d. Client accesses database server
Q33. Match each transmission medium with its upper-limit distance.
i. UTP
ii. Wireless
iii. Single-mode fiber
iv. Multimode fiber
a. 2 km
b. 100 m
c. 90 km
d. 500 m
Q34. True or false: IP phones and LAN switches can reassign a frame’s CoS bits.
Q35. Name two ways to reduce multicast traffic in the access layer.
Q36. What are two VLAN methods you can use to carry marking CoS on frames?
Q37. True or false: You can configure both CGMP and IGMP snooping in mixed Cisco switch and non-Cisco router environments.
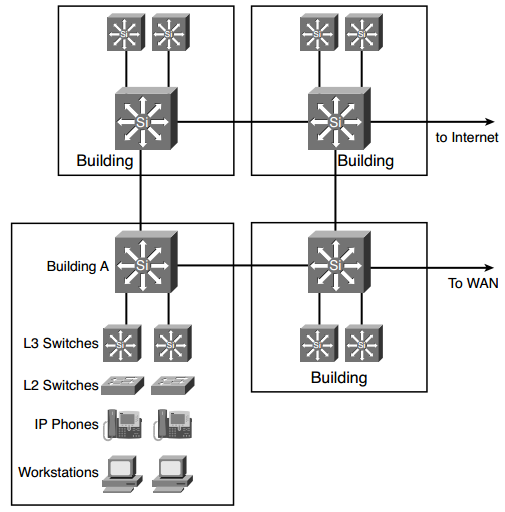
Use Below Figure to answer questions 38-43
Q38. What medium do you recommend for the campus LAN backbone?
Answer: The campus backbone should have high-speed links. Recommend Gigabit Ethernet links.
Q39. The workstations send frames with the DSCP set to EF. What should the IP phones do so that the network gives preference to VoIP traffic over data traffic?
Q40. If the Layer 2 switches in Building A cannot look at CoS and ToS fields, where should these fields be inspected for acceptance or reclassification: in the building Layer 3 switches or in the backbone Layer 3 switches?
Q41. Does the network have redundant access to the WAN?
Q42. Does the network have redundant access to the Internet?
Q43. Does Figure use recommended devices for networks designed using the Enterprise Architecture model?
Q44. Which are environmental characteristics? (Select three.)
a. Transmission media characteristics
b. Application characteristics
c. Distribution of network nodes
d. Operating system used
e. Remote-site connectivity requirements
Q45. Which network application type is most stringent on the network resources?
a. Peer to peer
b. Client to local server
c. Client to server farm
d. Client to enterprise edge
Q46. An application used by some users in a department generates significant amounts of bandwidth. Which is a best design choice?
a. Rewrite the application to reduce bandwidth.
b. Use Gigabit Ethernet connections for those users.
c. Put the application users into a separate broadcast domain.
d. Add several switches and divide the users into the two.
Q47. Users access servers located on a server VLAN and servers located in departmental VLANs. Users are located in the departmental VLAN. What is the expected traffic flow from users to servers?
a. Most traffic is local.
b. All traffic requires multilayer switching.
c. There is no need for multilayer switching.
d. Most of the traffic will have to be multilayer switched.
Q48. Company departments are located across several buildings? These departments use several common servers. Network policy and security are important. Where should servers be placed?
a. Within all department buildings and duplicate the common servers in each building.
b. Connect the common servers to the campus core.
c. Use a server farm.
d. Connect the servers to the distribution layer.
Q49. A large company has a campus core. What is the best practice for the core campus network?
a. Use triangles.
b. Use squares.
c. Use rectangles.
d. Use point-to-point mesh.
Q50. A company has five floors. It has Layer 2 switches in each floor with servers. They plan move servers to a new computer room and create a server farm. What should they use?
a. Replace all Layer 2 switches with Layer 3 switches.
b. Connect the Layer 2 switches to a Layer 3 switch in the computer room.
c. Connect the Layer 2 switches to a new Layer 2 switch in the computer room.
d. Connect the Layer 2 switches to each other.
Q51. A Fast Ethernet uplink is running at 80 percent utilization. Business-critical applications are used. What can be used to minimize packet delay and loss?
a. Implement QoS with classification and policing in the distribution layer.
b. Add additional VLANs so that the business applications are used on PCs on that VLAN.
c. Perform packet bit rewrite in the distribution switches.
d. Classify users in the access with different priority bits.
Q52. Which are four best practices used in the access layer?
a. Disable trunking in host ports.
b. Limit VLANS to one closet.
c. Use PVST+ as the STP with multilayer switches.
d. Enable trunking on host ports.
e. Use VLAN spanning to speed convergence of STP.
f. Use VTP Server mode in hierarchical networks.
g. Use VTP Transparent mode in hierarchical networks.
h. Use RPVST+ as the STP with multilayer switches.
Q53. Which are three best practices used in the distribution layer?
a. Use HSRP or GLBP.
b. Provide fast transport.
c. Use Layer 3 routing protocols to the core.
d. Use Layer 2 routing protocols to the core.
e. Summarize routes to the core layer.
f. Summarize routes to the access layer.
Q54. Which are four best practices used in the distribution layer?
a. Disable trunking in host ports.
b. Limit VLANS to one closet.
c. Use HSRP.
d. Use GLBP.
e. Use VLAN spanning to speed convergence of STP.
f. Use Layer 3 routing to the core.
g. Summarize routes.
h. Use RPVST+ as the STP with multilayer switches.
Q55. Which are three best practices used in the core layer?
a. Use routing with no Layer 2 loops.
b. Limit VLANS to one closet.
c. Use HSRP.
d. Use GLBP.
e. Use Layer 3 switches with fast forwarding.
f. Use Layer 3 routing to the core.
g. Use two equal-cost paths to every destination network.
h. Use RPVST+ as the STP with multilayer switches.
Q56. Match each enterprise campus component with its description.
i. Campus infrastructure
ii. Server farm
iii. Edge distribution
a. Consists of backbone, building-distribution, and building-access modules
b. Connects the campus backbone to the Enterprise Edge
c. Provides redundancy access to the servers
Q57. Why is LAN switching used more than shared LAN technology? (Select two.)
a. Shared LANs do not consume all available bandwidth.
b. Switched LANs offer increased throughput.
c. Switched LANs allow two or more ports to communicate simultaneously.
d. Switched LANs forward frames to all ports simultaneously.
Q58. What OSI layer does a bridge operate?
Q59. The 10Base2 Ethernet media is commonly referred as?
Q60. What is the recommended maximum number of nodes that should be used in a multiprotocol LAN segment?
Q61. Bridges control collision domains, broadcast domains, or both?
Q62. What is the maximum segment size in a 100BaseT network?
Q63. What is the maximum segment size in a 10Base2 network?
Q64. Routers operate on what OSI layer?
Q65. Fast Ethernet is covered by which IEEE standard?
Q66. What is 10Base5 commonly referred to as?
Q67. What device controls a broadcast domain?
Q68. What is the maximum segment size in 10BaseT?
Q69. What is the maximum segment size in 10Base2?
Q70. What is the maximum segment size in 10Base5?
Q71. What is the maximum segment size in 100BaseT?
Q72. What is the maximum segment size in 1000BaseT?
Q73. What does the acronym DIX stands for?
Q74. What are the three layers of hierarchical design?
Q75. At what percent utilization are Ethernets over-utilized?
Q76. At what percent utilization are Token Ring networks over-utilized?
Q77. At what percent utilization are FDDI networks over-utilized?
Q78. What is the maximum recommended percentage of broadcasts on the network?
Q79. What is the standard(s) for Gigabit Ethernet?
Q80. What standard governs Token Ring?
Q81. What media implements a dual-ring and forwards tokens?
Q82. Routers operate on which layer of the OSI model?
Q83. Switches operate on which layer of the OSI model?
Q84. Repeaters operate on which layer of the OSI model?
Q85. Bridges operate on which layer of the OSI model?
Q86. Transceivers operate on which layer of the OSI model?
Q87. Are bridges protocol transparent?
Q88. When switches implement cut-through switching mode, what is not verified to check for frame errors?
Q89. True or False: A repeater keeps a table of each MAC address on its ports and forwards frames accordingly.
Q90. True or False: Routers forward frames based on the destination MAC address.
Q91. True or False: Bridges forward frames based on the source MAC address.
Q92. What LAN media uses dual counter rotating rings?
Q93. Which Cisco device provides 48 ports of 10/100 Ethernet with 2 Gb uplinks?
Q94. What are the components of the three-part firewall system?
Q95. What is the encoding scheme of 10-Mbps Ethernet?
Q96. What is the encoding scheme of Token Ring?
Q97. 100BaseT forwards frames at what speed?
More Resources